3 levels of management in an organization – In the dynamic world of organizations, the concept of 3 levels of management stands as a cornerstone, shaping the structure and driving the success of countless enterprises. Each level, from top to bottom, plays a crucial role in the decision-making, communication, and execution that propel organizations forward.
Delving into the intricacies of this hierarchical framework, we’ll explore the distinct roles and responsibilities of each level, the communication and collaboration patterns that connect them, and the decision-making authority that empowers them. Along the way, we’ll uncover the challenges and opportunities that come with managing multiple levels of management, providing valuable insights for organizations seeking to optimize their structures.
Levels of Management
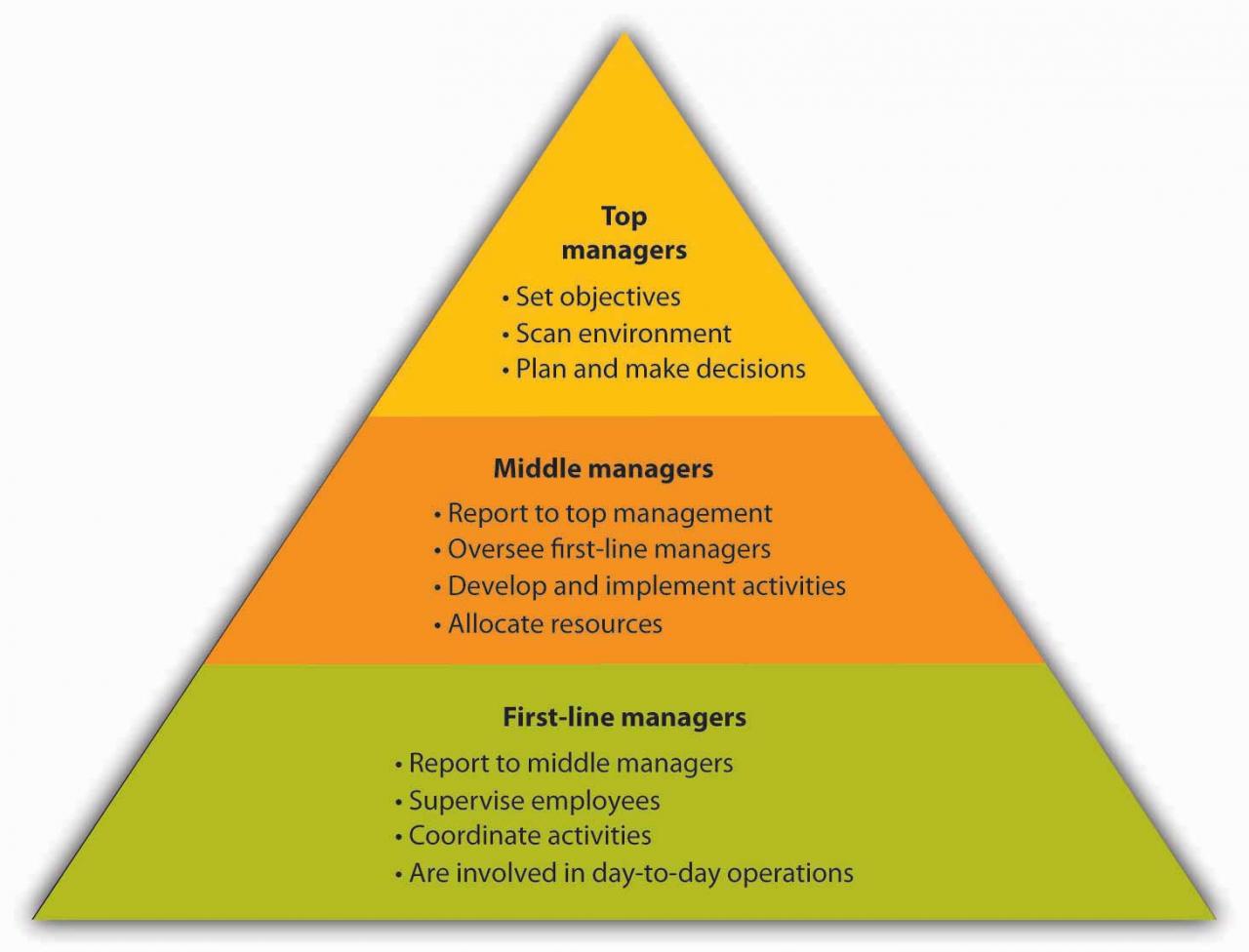
The management structure of an organization typically consists of three distinct levels: top-level management, middle-level management, and first-line management. Each level has its own unique roles, responsibilities, and decision-making authority.
The following diagram provides a visual representation of the three levels of management:
- Top-Level Management
- Middle-Level Management
- First-Line Management
Some examples of organizations that have implemented this three-level management structure include:
- Amazon
- Apple
- Walmart
Roles and Responsibilities, 3 levels of management in an organization
Top-level management is responsible for setting the overall direction and strategy of the organization. They make high-level decisions that impact the entire organization, such as mergers and acquisitions, product development, and marketing campaigns.
Middle-level management is responsible for implementing the strategies and plans developed by top-level management. They manage the day-to-day operations of the organization and oversee the work of first-line managers.
First-line management is responsible for supervising the work of employees and ensuring that they are meeting their performance goals. They provide feedback, training, and support to employees, and they are the first point of contact for employees who have questions or concerns.
The following table summarizes the key roles and responsibilities of each level of management:
| Level of Management | Roles and Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Top-Level Management |
|
| Middle-Level Management |
|
| First-Line Management |
|
Last Recap
In conclusion, the 3 levels of management serve as a vital foundation for organizational success. By understanding the roles, responsibilities, and interconnections of each level, organizations can foster effective communication, collaboration, and decision-making, ultimately driving productivity, innovation, and long-term growth.
General Inquiries: 3 Levels Of Management In An Organization
What are the key differences between the 3 levels of management?
The top level (senior management) focuses on strategic planning and overall direction, the middle level (middle management) manages operations and supervises lower-level employees, and the bottom level (first-line management) oversees daily tasks and directly interacts with employees.
How does communication flow between the different levels of management?
Communication typically flows downward, with top-level managers setting goals and objectives that are then communicated to middle and lower-level managers. Information and feedback also flow upward, providing senior management with insights from the front lines.
What factors influence the decision-making authority of each level of management?
Factors such as the size and complexity of the organization, the industry, and the level of trust and empowerment within the management team all impact the distribution of decision-making authority.