An employee is selected from a staff of 10 – In the competitive landscape of today’s job market, selecting the right employee from a pool of qualified candidates is crucial for any organization’s success. Join us as we delve into the intricate process of ‘Selecting an Employee from a Staff of 10’, exploring the essential steps, criteria, and techniques involved in making an informed and strategic decision.
From meticulously screening and interviewing potential candidates to conducting thorough reference checks and making objective selection decisions, we’ll provide a comprehensive roadmap to guide you through every stage of the employee selection process.
Employee Selection Process
The employee selection process involves identifying and hiring the most suitable candidate for a specific job opening. It typically comprises several steps designed to evaluate the skills, experience, and fit of potential employees.
Out of a staff of 10, one lucky employee gets the call to clock in. They hustle hard, putting in 15 hours of work and earning a cool $175. Not too shabby, right? Well, if you’re looking for more details on that sweet payday, check out this article . But back to our employee of the hour, they’re now enjoying their well-deserved break, feeling proud of a job well done.
The initial step is screening applicants based on their resumes and cover letters. This helps narrow down the pool of candidates to those who meet the minimum qualifications for the position.
Screening Process
- Reviewing resumes and cover letters for relevant skills and experience.
- Conducting phone screenings to assess communication skills and initial fit.
- Administering online assessments to evaluate cognitive abilities and personality traits.
Interview Process
Shortlisted candidates are typically invited for in-person or virtual interviews. These interviews provide an opportunity to assess their technical skills, problem-solving abilities, and cultural fit.
- Conducting structured interviews with standardized questions to ensure fairness.
- Using behavioral interviewing techniques to elicit specific examples of past performance.
- Involving multiple interviewers to gather diverse perspectives and reduce bias.
Assessments and Background Checks
In addition to interviews, employers may use assessments and background checks to further evaluate candidates.
- Administering cognitive ability tests to measure intelligence, problem-solving, and decision-making skills.
- Conducting personality assessments to identify traits relevant to job performance.
- Performing reference checks to verify past employment and performance.
- Running criminal background checks to ensure compliance with legal requirements and company policies.
By following a rigorous and standardized selection process, employers can increase the likelihood of hiring the most qualified and suitable candidates for their open positions.
Criteria for Employee Selection
The selection of the most suitable candidate for a job position is a crucial process that requires careful consideration of various criteria. These criteria serve as the foundation for evaluating candidates and making informed decisions about their potential fit for the role and the organization.
Job-Related Skills, Experience, and Qualifications
One of the primary criteria used in employee selection is job-related skills, experience, and qualifications. These factors are essential in determining a candidate’s ability to perform the tasks and responsibilities associated with the position. Skills refer to the specific abilities and knowledge required to execute the job effectively, while experience denotes the practical application of those skills in relevant work environments.
Qualifications, such as educational degrees, certifications, or licenses, provide evidence of a candidate’s formal training and expertise in the field.
Organizations often establish minimum requirements for job-related skills, experience, and qualifications to ensure that candidates possess the necessary foundation for success in the role. These requirements are typically Artikeld in job descriptions and serve as a benchmark for screening and evaluating candidates.
Let’s say you’re the boss and need to pick a new hire from your rad team of 10. You could post a job ad, but let’s get real – your employees are like your secret weapon. They know the drill and can give you the inside scoop on who’s got the right stuff.
That’s why employee referrals are the bomb for finding top talent. Back to our team of 10, if one of your peeps recommends someone, you know they’re gonna be a rockstar!
Personal Qualities and Cultural Fit, An employee is selected from a staff of 10
In addition to job-related criteria, personal qualities and cultural fit are also considered in the employee selection process. Personal qualities encompass an individual’s values, attitudes, and behaviors that influence their work style and interactions with others. Organizations seek candidates who exhibit traits such as integrity, teamwork, adaptability, and a strong work ethic.
Cultural fit refers to the alignment between a candidate’s values, beliefs, and behaviors with the organization’s culture. A good cultural fit can contribute to employee satisfaction, job performance, and organizational commitment. Organizations often assess cultural fit through interviews, reference checks, and other methods to ensure that candidates share similar values and perspectives.
Out of a staff of 10, one lucky employee will be selected for a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity: to shadow a notary who is an employee of a bank . This is a huge honor, and the chosen employee will get to learn the ins and outs of this fascinating profession.
But back to our original topic, the selection process for this esteemed opportunity from a staff of 10 is sure to be rigorous and competitive.
Interview Techniques
Interviewing is a crucial step in the employee selection process. It allows employers to assess candidates’ qualifications, skills, and fit for the position. There are various types of interviews used, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Structured Interviews
Structured interviews follow a predetermined set of questions asked to all candidates in the same order. This format ensures fairness and consistency in the evaluation process. Structured interviews are particularly useful for comparing candidates with similar backgrounds and qualifications.
Unstructured Interviews
Unstructured interviews allow interviewers more flexibility in the questions they ask and the order in which they are asked. This approach gives interviewers the opportunity to explore areas of interest or concern that may not be covered in a structured interview.
However, unstructured interviews can be more subjective and less reliable than structured interviews.
Out of a staff of 10, one employee is chosen, and they’re in for a treat. Every employee has certain rights, like the right to a safe workplace, fair pay, and a chance to voice their concerns. These are just a few of the 5 rights of an employee . Knowing these rights can help the chosen employee make the most of their new position.
Panel Interviews
Panel interviews involve multiple interviewers, each with a specific area of expertise or perspective. This format allows for a more comprehensive evaluation of candidates and can help reduce bias. Panel interviews can be more intimidating for candidates, but they also provide the opportunity to interact with multiple individuals who will be involved in the decision-making process.
Imagine this: You’re the lucky one picked from a team of 10. Now, you’ve got some serious responsibilities to shoulder, like understanding your 4 responsibilities as an employee . But don’t sweat it, you’re the chosen one for a reason.
So, go ahead, show ’em what you’re made of!
Phone Interviews
Phone interviews are typically used as a screening tool to narrow down the pool of candidates. They are less formal than in-person interviews and can be conducted over the phone or video call. Phone interviews are convenient and cost-effective but may not provide as much information about candidates as in-person interviews.
Behavioral Interviews
Behavioral interviews focus on candidates’ past experiences and behaviors to predict their future performance. Interviewers ask candidates to describe specific situations they have encountered and how they handled them. This approach assumes that past behavior is a good indicator of future behavior.
Situational Judgment Tests
Situational judgment tests present candidates with hypothetical scenarios and ask them to choose the most appropriate response from a list of options. These tests are designed to assess candidates’ decision-making skills and their ability to handle different situations.
Reference Checks: An Employee Is Selected From A Staff Of 10
Conducting thorough reference checks is a crucial step in the employee selection process. It helps verify the accuracy of the candidate’s information and provides insights into their work ethic, skills, and character. Reference checks can help identify any potential red flags or inconsistencies that may not have been apparent during the interview stage.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to conduct reference checks effectively:
Obtaining References
- Request the candidate to provide a list of professional references, including former supervisors, colleagues, or clients.
- Ensure that the candidate has authorized you to contact these references.
Contacting References
- Contact each reference via phone, email, or video call.
- Introduce yourself and explain the purpose of the call.
- Ask specific questions about the candidate’s performance, skills, and work ethic.
Questions to Ask
- Can you describe the candidate’s strengths and weaknesses?
- How did the candidate perform in their previous role?
- What were the candidate’s key accomplishments?
- Did the candidate exhibit any areas where they need improvement?
- Would you recommend the candidate for this position?
Legal and Ethical Considerations
- Ensure that the reference checks are conducted fairly and without bias.
- Respect the privacy of the references and only ask questions that are relevant to the position.
- Document the results of the reference checks and keep them confidential.
Decision-Making Process
The final decision in the employee selection process is influenced by a combination of objective and subjective factors. Objective factors include the candidate’s qualifications, experience, and skills. Subjective factors include the interviewer’s personal preferences and biases.
Role of Bias and Subjectivity
Bias and subjectivity can play a significant role in the decision-making process. Interviewers may be biased towards candidates who are similar to them in terms of race, gender, or age. They may also be influenced by their own personal experiences and beliefs.
Making Objective and Fair Selection Decisions
To make objective and fair selection decisions, interviewers should be aware of their own biases and take steps to minimize their impact. They should also use a structured interview process that focuses on the candidate’s qualifications and experience. Additionally, they should consider using multiple interviewers to get a more well-rounded view of the candidate.
Communication with Candidates
Effective communication with candidates is crucial throughout the selection process. Open and timely communication fosters trust and transparency, enhancing the candidate experience.
Upon making a decision, it is essential to inform both successful and unsuccessful candidates promptly and professionally.
Successful Candidates
- Offer Details:Clearly Artikel the position, compensation, benefits, and start date.
- Next Steps:Provide instructions for accepting the offer, completing necessary paperwork, and scheduling any onboarding activities.
- Gratitude:Express appreciation for their interest and participation in the process.
Unsuccessful Candidates
- Thank-You Note:Send a personalized email or letter thanking them for their application and expressing gratitude for their time.
- Feedback:If appropriate, offer constructive feedback on their application or interview performance to help them improve for future opportunities.
- Stay in Touch:Encourage them to stay connected for potential future openings.
Clear and timely communication not only conveys the decision but also maintains a positive employer brand and leaves a lasting impression on candidates.
Handling Candidate Objections or Concerns
It is not uncommon for candidates to have questions or concerns about the selection decision. It is important to handle these objections professionally and empathetically.
- Listen Actively:Allow the candidate to express their concerns without interrupting.
- Provide Context:Explain the selection criteria and the reasons why the other candidate was chosen.
- Offer Alternatives:If possible, suggest alternative opportunities within the organization or refer them to other companies.
By addressing candidate objections effectively, you can maintain a positive relationship and minimize any negative impact on the candidate’s perception of the organization.
Onboarding Process
The onboarding process is a crucial step in welcoming and integrating a new employee into the organization. It involves a series of activities designed to provide the employee with the necessary knowledge, skills, and support to become a productive member of the team.
Let’s say you’re the boss and you’ve got a staff of 10. You need to pick one for a special project. How do you choose? Well, one way is to look at the advantages of an employee . What skills do they have? What experience? How well do they work with others? Once you’ve considered all of these factors, you can make an informed decision about who to choose.
An employee with the right skills and experience can make a big difference in the success of your project. So take your time and choose wisely.
A positive and informative onboarding experience is essential for several reasons. First, it helps the employee feel welcomed and valued, which can lead to increased job satisfaction and retention. Second, it provides the employee with the information and resources they need to succeed in their role.
When an employee is selected from a staff of 10, they are expected to uphold the company’s standards of conduct. If an employee engages in misconduct, they may receive a warning letter outlining the specific behavior that violated company policy.
The employee is then given an opportunity to correct their behavior and avoid further disciplinary action. An employee is selected from a staff of 10 because they are expected to be a valuable asset to the company and contribute to its success.
Finally, it helps the organization to establish a strong foundation for the employee’s future success.
Mentors and Training Programs
Mentors and training programs play a vital role in the onboarding process. Mentors can provide new employees with guidance and support, while training programs can provide them with the skills and knowledge they need to succeed in their role.
- Mentors can help new employees learn about the organization’s culture, values, and expectations.
- Mentors can provide new employees with advice and support on a variety of topics, such as career development, work-life balance, and personal growth.
- Training programs can provide new employees with the skills and knowledge they need to perform their jobs effectively.
- Training programs can help new employees to develop their professional skills and knowledge.
Performance Evaluation
Performance evaluations are essential tools for assessing employee performance and providing feedback to help them improve. They also play a crucial role in making informed decisions about promotions, compensation, and other aspects of employee management.
Designing and Conducting Effective Performance Evaluations
Effective performance evaluations should be:
- Objective:Based on clear and measurable criteria.
- Regular:Conducted at predetermined intervals throughout the year.
- Fair:Administered consistently across employees.
- Constructive:Focused on providing specific and actionable feedback.
- Collaborative:Involving both the employee and their supervisor.
Using Performance Evaluations for Employee Development and Decision-Making
Performance evaluations can be used to:
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement:Help employees understand their performance and set goals for growth.
- Make informed decisions about promotions and compensation:Provide data-driven insights into employee performance and potential.
- Provide feedback and coaching:Empower supervisors to give regular and specific feedback to employees.
- Identify training and development needs:Help organizations tailor training programs to address employee performance gaps.
Employee Development
Employee development refers to the deliberate efforts made by organizations to enhance the knowledge, skills, and abilities of their employees. This can be achieved through various opportunities, including formal training programs, on-the-job experiences, and informal learning initiatives. Investing in employee development is crucial for organizations to remain competitive, adapt to changing market demands, and retain valuable employees.
Benefits of Employee Development
- Enhanced employee performance and productivity
- Increased employee engagement and satisfaction
- Improved organizational efficiency and effectiveness
- Reduced employee turnover and increased loyalty
- Development of future leaders and successors
Creating a Comprehensive Employee Development Plan
Identify Development Needs
Conduct performance evaluations, skills assessments, and employee surveys to determine areas for improvement.
Set Development Goals
Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound goals aligned with organizational objectives.
One lucky employee was chosen from a staff of 10. They were recognized for their hard work and dedication, and they are truly an appreciated employee . The selection process was rigorous, but in the end, there was no doubt that this employee deserved the recognition.
They are a valuable asset to the team, and their contributions are greatly appreciated. Their selection is a testament to the importance of hard work and dedication.
Develop a Development Strategy
Choose appropriate development methods, such as training programs, mentoring, coaching, or on-the-job assignments.
Implement and Monitor Progress
Track employee participation, assess learning outcomes, and provide regular feedback.
Evaluate and Adjust
When an employee is selected from a staff of 10, their gross income is subject to various deductions. These deductions typically include federal and state income taxes, Social Security and Medicare taxes, and health insurance premiums. Understanding these deductions is crucial for employees to accurately estimate their take-home pay and plan their finances.
Ultimately, the selection of an employee from a staff of 10 is a critical decision that can impact the company’s overall performance and success.
Regularly review the development plan, make adjustments based on feedback and progress, and ensure alignment with organizational needs.
Employee Retention
Employee retention is crucial for the success of any organization. It refers to the ability of a company to retain its employees over a period of time, thereby reducing turnover and maintaining a stable workforce.
Numerous factors contribute to employee retention, including:
- Competitive compensation and benefits
- Opportunities for professional development and growth
- Positive and supportive work environment
- Strong company culture and values
- Work-life balance
Strategies for Improving Employee Retention Rates
To enhance employee retention rates, organizations can implement various strategies, such as:
- Conducting exit interviews to understand reasons for employee turnover
- Offering competitive compensation and benefits packages
- Providing opportunities for professional development and advancement
- Creating a positive and inclusive work environment
- Recognizing and rewarding employee achievements
- Encouraging work-life balance
Importance of Creating a Positive and Supportive Work Environment
A positive and supportive work environment is essential for employee retention. It fosters a sense of belonging and engagement, which motivates employees to stay with the organization.
Key elements of a positive work environment include:
- Open communication and transparency
- Respectful and collaborative relationships
- Opportunities for employee input and feedback
- Recognition and appreciation for employee contributions
- Support for work-life balance
By creating a positive and supportive work environment, organizations can enhance employee retention, boost morale, and improve overall organizational performance.
Legal Considerations
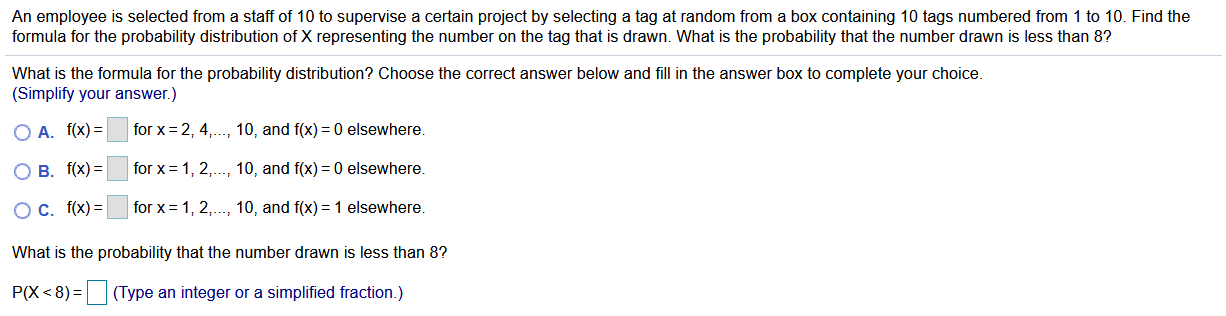
The employee selection process is subject to a complex web of legal regulations and statutes. It is crucial for organizations to adhere to these laws to avoid potential legal complications and ensure fairness and equity in the hiring process.
One of the most significant legal considerations is compliance with equal opportunity and non-discrimination laws. These laws prohibit employers from discriminating against applicants based on protected characteristics such as race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age, disability, or genetic information.
Avoiding Legal Pitfalls
To avoid potential legal pitfalls, organizations should implement the following measures:
- Develop clear and objective job descriptions and selection criteria.
- Use standardized interview questions and evaluation methods for all candidates.
- Document all aspects of the selection process, including interview notes and reference checks.
- Train hiring managers on equal opportunity and non-discrimination laws.
- Establish a grievance procedure for candidates who believe they have been discriminated against.
Epilogue

As we conclude our exploration of ‘Selecting an Employee from a Staff of 10’, it’s evident that this process demands a delicate balance of objectivity, fairness, and strategic decision-making. By adhering to the principles Artikeld in this guide, organizations can confidently navigate the complexities of employee selection, securing the talent they need to drive their business forward and achieve lasting success.
FAQ Summary
What are the key steps involved in selecting an employee from a staff of 10?
The employee selection process typically involves screening candidates, conducting interviews, evaluating assessments, and performing background checks.
What criteria should be considered when evaluating candidates?
Key criteria include job-related skills, experience, qualifications, personal qualities, and cultural fit.
How can organizations avoid bias and subjectivity in the decision-making process?
Using structured interviews, standardized evaluation criteria, and involving multiple interviewers can help mitigate bias.