A company purchases an asset for 10000 – When a company purchases an asset for $10,000, it sets the stage for an intriguing narrative that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This guide will delve into the intricacies of asset acquisition, providing a comprehensive overview of the topic for readers who seek to gain a deeper understanding of this essential business practice.
From explaining the concept of asset acquisition and discussing the various types of assets that companies can purchase, to examining the reasons why companies make these purchases, this guide covers all the fundamental aspects of asset acquisition. Additionally, it explores the accounting treatment for asset purchases, providing examples of journal entries to record these transactions and discussing their impact on financial statements.
Asset Purchase Overview
When a company acquires an asset, it gains ownership and control over a resource that has economic value and a useful life extending beyond the current accounting period. Assets can be tangible, such as buildings, equipment, or inventory, or intangible, such as patents, trademarks, or goodwill.
Companies purchase assets for a variety of reasons, including:
- To increase production capacity
- To improve efficiency and reduce costs
- To gain a competitive advantage
- To meet customer demand
Types of Assets
There are many different types of assets that companies can purchase, including:
- Fixed assets:These are long-term assets that are not easily converted into cash, such as land, buildings, and equipment.
- Current assets:These are short-term assets that can be easily converted into cash, such as inventory, accounts receivable, and cash.
- Intangible assets:These are assets that do not have a physical form, such as patents, trademarks, and goodwill.
Accounting for Asset Purchases
Accounting for asset purchases involves recognizing and recording the acquisition of assets on the balance sheet. Assets are economic resources that are owned or controlled by a company and are expected to provide future economic benefits. When a company purchases an asset, it must record the transaction in its accounting records to accurately reflect its financial position.
The accounting treatment for asset purchases depends on the type of asset acquired. Common types of assets include fixed assets, such as property, plant, and equipment, and current assets, such as inventory and accounts receivable. The cost of the asset is typically recorded as a debit to the appropriate asset account and a credit to cash or accounts payable.
Journal Entries for Asset Purchases
The following are examples of journal entries to record asset purchases:
- Fixed Asset Purchase:
- Debit: Equipment $10,000
- Credit: Cash $10,000
- Current Asset Purchase:
- Debit: Inventory $5,000
- Credit: Accounts Payable $5,000
Impact of Asset Purchases on Financial Statements
Asset purchases have a significant impact on a company’s financial statements. The purchase of fixed assets increases the company’s total assets and may also increase its depreciation expense over time. The purchase of current assets increases the company’s liquidity and working capital.
A company may purchase an asset for $10,000, but did you know that you can’t FaceTime on an Android device? Can I FaceTime on an Android Device ? That’s right, the popular video calling app is only available on Apple devices.
However, there are a few workarounds that you can use to FaceTime on an Android device. One option is to use a third-party app like Google Duo or Skype. Another option is to use a web-based FaceTime client. Finally, you can also use an Android emulator to run FaceTime on your computer.
Additionally, asset purchases can impact a company’s financial ratios, such as the debt-to-asset ratio and the current ratio.
Methods of Asset Acquisition
Acquiring assets is crucial for businesses to expand their operations and meet customer demands. There are various methods of asset acquisition, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these methods allows businesses to make informed decisions that align with their financial capabilities and long-term goals.
Cash Purchases
Cash purchases involve paying the full cost of an asset upfront in cash. This method is straightforward and provides immediate ownership of the asset. Advantages include:
- No interest payments or financing costs
- Simple and quick transaction process
- Potential for discounts or negotiations
However, cash purchases can deplete a company’s cash reserves, especially for large acquisitions.
When a company purchases an asset for $10,000, they are essentially buying something of value that will benefit their business. For instance, you might wonder can i get my itunes on an android . That’s a great question! The answer is yes, you can get your iTunes on an Android device.
There are a few different ways to do this, but the most common way is to use a third-party app. Once you have iTunes on your Android device, you can access all of your music, movies, and TV shows. You can also sync your iTunes library with your Android device, so you can have all of your content in one place.
Returning to the topic of purchasing assets, companies do this to increase their value and improve their bottom line.
Installment Purchases
Installment purchases allow businesses to spread the cost of an asset over a period of time through regular payments. This method is suitable when a company has limited cash on hand or prefers to preserve its cash flow. Advantages include:
- Conserves cash reserves
- Predictable payment schedule
- Interest rates may be lower than other financing options
Disadvantages include:
- Interest charges accumulate over time
- Can lead to higher overall costs compared to cash purchases
Leases
Leases provide a way for businesses to use an asset without purchasing it outright. Under a lease agreement, a company rents the asset from a lessor for a specified period. Advantages include:
- Preserves capital and cash flow
- Lower upfront costs compared to purchases
- Flexibility to upgrade or replace assets at the end of the lease term
Disadvantages include:
- No ownership of the asset
- Potential for higher long-term costs than purchases
- Restrictions on asset use or modifications
The choice of asset acquisition method depends on several factors, including the availability of cash, the size of the acquisition, and the company’s long-term financial strategy. By carefully considering the advantages and disadvantages of each method, businesses can make informed decisions that support their growth and profitability.
Let’s say a company decides to splurge and drop 10 grand on a shiny new asset. Now, that’s a pretty sweet deal, but hold up! Before you start counting your cash, let’s take a quick detour to the world of tech.
Wondering if those fancy Apple AirPods will work with your Android phone? Can I use Apple AirPods with an Android phone ? Back to our asset purchase, that 10K is gonna set you up for success.
Asset Valuation
Determining the fair value of assets is crucial for various financial reporting purposes. Asset valuation helps businesses make informed decisions about their investments, facilitates accurate financial reporting, and ensures compliance with accounting standards.
Several methods are used for asset valuation, each with its advantages and limitations. These include:
Historical Cost
This method records the asset at its original purchase price. It is straightforward to apply but may not reflect the current fair value of the asset.
Fair Value
Fair value represents the estimated market value of the asset. It is often determined through appraisals or market research.
Replacement Cost
This method estimates the cost of replacing the asset with a similar one of equal utility. It considers the current market value of the asset and any depreciation.
Factors that affect asset valuation include:
- Market conditions
- Asset condition
- Expected future cash flows
- Legal and regulatory factors
Depreciation and Amortization
In the world of accounting, assets lose their value over time. Think of it like your favorite pair of jeans – they might look great at first, but after a few washes, they’re not quite as sharp. That’s where depreciation and amortization come in.
They’re accounting techniques that spread out the cost of an asset over its useful life, just like spreading the cost of those jeans over the number of times you wear them.
Depreciation is for tangible assets, like buildings or equipment. Amortization is for intangible assets, like patents or trademarks. Both methods reduce the asset’s value on the balance sheet and create an expense on the income statement.
The company bought an asset for 10,000 bucks, which is pretty dope. Speaking of dope, did you know that you can’t FaceTime from an Android phone to an iPhone? Can I FaceTime from an Android Phone to an iPhone is the ultimate guide to help you stay connected, even if your friends are on the other side of the green bubble divide.
And hey, who needs FaceTime when you can just buy another asset for 10,000, right?
Methods of Depreciation and Amortization
There are different ways to calculate depreciation and amortization. Some common methods include:
- Straight-line method: Spreads the cost evenly over the asset’s useful life.
- Declining-balance method: Depreciates the asset more heavily in the early years of its life.
- Units-of-production method: Depreciates the asset based on how much it’s used.
Impact on Financial Statements
Depreciation and amortization have a significant impact on financial statements. They:
- Reduce the asset’s value on the balance sheet.
- Create an expense on the income statement, which reduces net income.
- Affect cash flow by reducing taxable income, which can lead to lower tax payments.
Asset Impairment
Asset impairment refers to the permanent decline in the value of an asset below its carrying amount on the balance sheet. It occurs when the fair value of an asset is less than its book value.
Various factors can lead to asset impairment, including:
- Technological obsolescence
- Market changes
- Physical damage
- Legal or regulatory changes
Assessing and Recording Asset Impairment
To assess asset impairment, companies compare the fair value of an asset to its carrying amount. If the fair value is less than the carrying amount, an impairment loss is recognized on the income statement.
The following steps are involved in recording asset impairment:
- Identify the impaired asset.
- Determine the fair value of the asset.
- Calculate the impairment loss as the difference between the carrying amount and the fair value.
- Record the impairment loss on the income statement.
- Reduce the carrying amount of the asset to the fair value.
Asset Disposal
Asset disposal involves the process of getting rid of an asset that is no longer needed or useful to the company. There are several methods of asset disposal, each with its own accounting treatment.
Methods of Asset Disposal
- Sale:When an asset is sold, the company recognizes a gain or loss on the disposal. The gain or loss is calculated as the difference between the sale price and the book value of the asset.
- Retirement:When an asset is retired, it is removed from service and no longer used by the company. The company recognizes a loss on the disposal equal to the book value of the asset.
- Abandonment:When an asset is abandoned, it is discarded and no longer has any value to the company. The company recognizes a loss on the disposal equal to the book value of the asset.
Accounting Treatment for Asset Disposals
The accounting treatment for asset disposals depends on the method of disposal used.
- Sale:When an asset is sold, the company debits cash for the sale price and credits the asset account for the book value of the asset. The difference between the sale price and the book value is recognized as a gain or loss on the disposal.
- Retirement:When an asset is retired, the company debits the accumulated depreciation account for the accumulated depreciation on the asset and credits the asset account for the book value of the asset. The difference between the book value and the accumulated depreciation is recognized as a loss on the disposal.
- Abandonment:When an asset is abandoned, the company debits the accumulated depreciation account for the accumulated depreciation on the asset and credits the asset account for the book value of the asset. The difference between the book value and the accumulated depreciation is recognized as a loss on the disposal.
Examples of Asset Disposals
- A company sells a piece of equipment for $10,000. The book value of the equipment is $8,000. The company recognizes a gain on the disposal of $2,000.
- A company retires a building that has a book value of $100,000. The company recognizes a loss on the disposal of $100,000.
- A company abandons a piece of land that has a book value of $50,000. The company recognizes a loss on the disposal of $50,000.
Asset Management: A Company Purchases An Asset For 10000
Asset management is a crucial process that enables organizations to optimize the utilization, maintenance, and disposition of their assets. It involves planning, organizing, and controlling assets to maximize their value and minimize risks.
Yo, check this out! A company just dropped 10 grand on a new asset. It’s like, the latest and greatest thing. They even have an API that’s like, super sick. It can get real-time data straight from the source . Now they’re like, the king of the castle.
But seriously, that 10K investment is gonna pay off big time!
There are several asset management strategies that organizations can adopt. Some common strategies include:
Asset Lifecycle Management
- Involves tracking and managing assets throughout their entire lifecycle, from acquisition to disposal.
- Helps organizations optimize asset performance, minimize downtime, and maximize asset value.
Preventive Maintenance
- Involves performing regular maintenance tasks to prevent asset failures and extend their lifespan.
- Reduces the risk of unexpected breakdowns, improves asset reliability, and minimizes maintenance costs.
Predictive Maintenance
- Uses data analytics to monitor asset condition and predict potential failures.
- Enables organizations to schedule maintenance proactively, reducing downtime and improving asset utilization.
Asset Tracking, A company purchases an asset for 10000
- Involves using technology to track and monitor assets in real-time.
- Provides visibility into asset location, usage, and condition, enabling better decision-making.
Asset Disposal
- Involves selling, scrapping, or donating assets that are no longer needed.
- Helps organizations recover value from obsolete or underutilized assets and reduce disposal costs.
Asset Financing
Asset financing refers to the various methods used by companies to acquire assets without using their own cash on hand. These methods involve obtaining funds from external sources to finance the purchase or lease of assets.
There are three primary methods of asset financing: debt financing, equity financing, and leasing.
Debt Financing
- Debt financing involves borrowing money from a lender, such as a bank or financial institution, and using the borrowed funds to purchase an asset.
- The loan is typically secured by the asset itself, meaning that if the borrower defaults on the loan, the lender can seize the asset.
- Debt financing is a common method of financing for large assets, such as real estate or equipment.
Equity Financing
- Equity financing involves selling shares of ownership in the company to investors in exchange for cash.
- The investors become shareholders in the company and are entitled to a share of the company’s profits.
- Equity financing is a good option for companies that need to raise a large amount of capital quickly.
Leasing
- Leasing involves renting an asset from a lessor for a specified period of time.
- The lessee (the company renting the asset) makes regular payments to the lessor.
- At the end of the lease term, the lessee can return the asset to the lessor, purchase the asset, or renew the lease.
Asset Reporting
Asset reporting is crucial for organizations to maintain transparency, accountability, and financial health. It involves disclosing information about the company’s assets, their acquisition, valuation, and management.
Asset reporting is essential for several reasons. First, it helps investors and creditors assess the financial stability and performance of a company. Second, it assists management in making informed decisions about asset allocation and utilization. Third, it ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and accounting standards.
Different Asset Reporting Requirements
Asset reporting requirements vary depending on the organization’s size, industry, and legal jurisdiction. Generally, companies are required to disclose information about their assets in their financial statements, including the balance sheet and notes to the financial statements.
The company’s recent acquisition of an asset for $10,000 has raised questions about security. In this day and age, it’s important to consider the possibility of cyberattacks. For example, can an android phone be hacked remotely ? With the advancement of technology, it’s crucial to take precautions to protect sensitive data and assets.
The company’s investment in security measures will undoubtedly enhance its overall resilience and safeguard its valuable assets.
- Balance Sheet:The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It includes a list of the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Notes to the Financial Statements:The notes to the financial statements provide additional information about the company’s assets, including their acquisition, valuation, and management.
Preparing Asset Reports
Asset reports can be prepared using various methods, including:
- Physical Inventory:This involves physically counting and verifying the existence of assets.
- Asset Registers:These are databases that track the acquisition, valuation, and disposition of assets.
- Software:There are specialized software programs available to assist with asset reporting.
The method used to prepare asset reports will depend on the size and complexity of the organization.
Asset Case Study
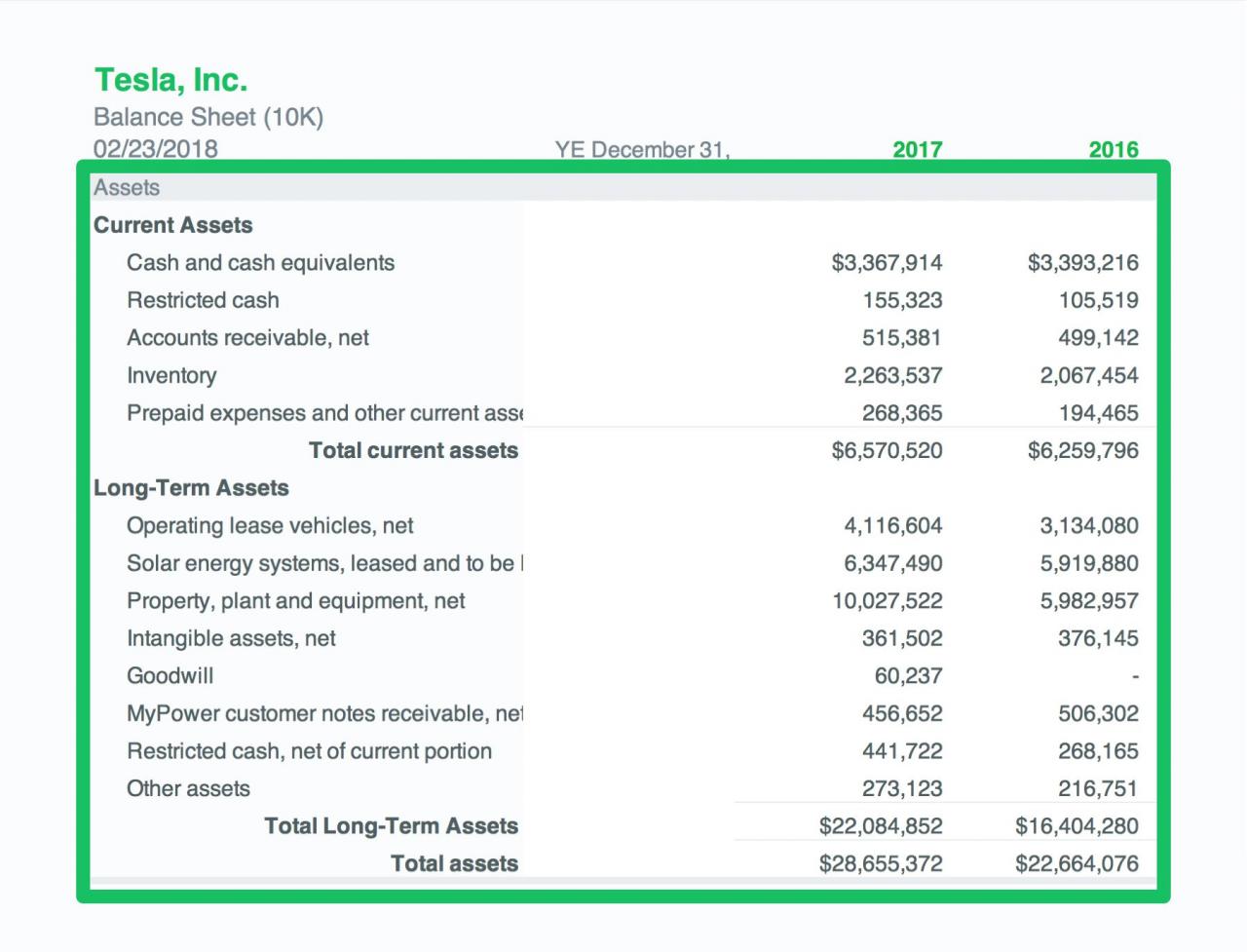
In 2022, ABC Corporation, a leading manufacturer of electronics, decided to purchase a new automated assembly line for $10,000,This decision was driven by several factors, including:
Increased demand for products
ABC Corporation had experienced a surge in demand for its products, particularly in the smartphone and tablet markets. The company needed to increase its production capacity to meet this demand.
Aging equipment
The company’s existing assembly lines were aging and becoming less efficient. The new automated assembly line would allow ABC Corporation to improve its productivity and reduce its manufacturing costs.
Technological advancements
The new automated assembly line incorporated the latest technological advancements, which would allow ABC Corporation to produce higher-quality products more efficiently.
The purchase of the new automated assembly line had a significant impact on ABC Corporation’s financial performance. In the first year of operation, the company experienced a 15% increase in production output and a 10% decrease in manufacturing costs. This led to a significant increase in profitability for ABC Corporation.
Factors Influencing Asset Purchase Decisions
Several factors influence a company’s decision to purchase an asset, including:
Strategic alignment
The asset should align with the company’s long-term strategic goals and objectives.
Financial viability
The company should have the financial resources to purchase and maintain the asset.
Operational efficiency
The asset should improve the company’s operational efficiency and productivity.
Risk assessment
A company purchases an asset for 10000. Meanwhile, the eternal question arises: can apple air tags be used with an android phone ? Back to our asset purchase, the company must now depreciate the asset over its useful life.
The company should assess the risks associated with the asset purchase and develop mitigation strategies.
Impact of Asset Purchases on Financial Performance
The purchase of an asset can have a significant impact on a company’s financial performance, including:
Increased profitability
Assets can help a company increase its profitability by improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and generating revenue.
Improved cash flow
Assets can help a company improve its cash flow by generating revenue or reducing expenses.
Enhanced financial stability
Assets can help a company enhance its financial stability by providing a source of collateral for loans or investments.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, the purchase of an asset for $10,000 is a significant event for any company. By understanding the concepts and processes involved in asset acquisition, companies can make informed decisions that will contribute to their long-term success. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of this topic, empowering readers with the knowledge they need to navigate the complexities of asset acquisition and maximize the value of their investments.
Detailed FAQs
What is the definition of asset acquisition?
Asset acquisition refers to the process by which a company obtains ownership of an asset, which can include tangible assets such as property, plant, and equipment, as well as intangible assets such as patents, trademarks, and copyrights.
What are the different methods of asset acquisition?
Companies can acquire assets through various methods, including cash purchases, installment purchases, and leases. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method will depend on the specific circumstances of the transaction.
How is the purchase of an asset recorded in the accounting records?
When a company purchases an asset, the transaction is recorded in the accounting records by debiting the asset account and crediting the cash or other consideration paid for the asset.
What is the purpose of depreciation and amortization?
Depreciation and amortization are accounting methods used to allocate the cost of an asset over its useful life. Depreciation is used for tangible assets, while amortization is used for intangible assets.
What are the different types of asset management strategies?
There are various asset management strategies that companies can implement, including preventive maintenance, predictive maintenance, and risk-based maintenance. The choice of strategy will depend on the specific assets and the company’s overall risk tolerance.