When an economics class formed a company, they embarked on an extraordinary journey that blurred the lines between academia and the business world. This audacious endeavor not only challenged conventional norms but also ignited a passion for innovation and entrepreneurship among its student founders.
Throughout their adventure, they navigated the complexities of company formation, business plan development, and product or service creation. They grappled with the intricacies of marketing, sales, and financial management, while adhering to legal and regulatory requirements. Along the way, they encountered both triumphs and setbacks, but their unwavering determination propelled them forward.
Company Formation
Company formation involves establishing a legal entity to conduct business. It entails several steps:1.
-
-*Choose a Business Entity
Determine the most suitable business structure, such as sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability company (LLC), or corporation.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
-*Name the Company
Select a distinctive and memorable name that reflects the business’s identity.
-*Register the Company
File the necessary paperwork with the appropriate government agencies, such as the Secretary of State or the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
An economics class took the plunge and formed their own company, learning firsthand the ins and outs of business. As they delved deeper, they discovered that a joint stock company, like the one they had formed, is considered an “artificial person” in the eyes of the law ( a joint stock company is an artificial person ). This concept opened their eyes to the legal and financial implications of their venture, as their company became a separate entity from its individual members.
-*Obtain Licenses and Permits
Acquire any required licenses or permits specific to the business’s industry and location.
-*Open a Business Bank Account
Establish a dedicated bank account for the company’s financial transactions.
-*Hire Employees
Recruit and hire employees if necessary, ensuring compliance with labor laws and regulations.
Types of Business Entities
There are various types of business entities, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
-
-*Sole Proprietorship
A business owned and operated by a single individual with unlimited liability.
-*Partnership
A business owned by two or more individuals who share profits and liabilities.
-*Limited Liability Company (LLC)
A hybrid business structure that provides limited liability to its owners while allowing for pass-through taxation.
-*Corporation
A legal entity separate from its owners, offering limited liability and the ability to raise capital through stock issuance.
Economics Students Forming Companies
Economics students have successfully formed companies, leveraging their knowledge and skills in:
-
-*Market Analysis
Conducting thorough research to identify market opportunities and target customers.
-*Financial Planning
Creating financial models and projections to ensure financial viability.
-*Business Strategy
Developing comprehensive business plans that Artikel the company’s goals, strategies, and operations.
-*Negotiation
Negotiating contracts and agreements with vendors, customers, and other stakeholders.
-*Leadership
Leading teams, managing operations, and making sound business decisions.
Business Plan Development
Crafting a comprehensive business plan is essential for guiding your company’s direction and ensuring its success. This plan serves as a roadmap, outlining your business goals, strategies, and financial projections.
An economics class at our local high school formed a company to learn about business. They’re learning about everything from marketing to finance. One of the things they’re learning about is a financial agreement between an insurance company and an individual . This is an important topic for them to learn about because it’s something that they’ll all need to know about as adults.
Key Components of a Business Plan
- Executive Summary: A concise overview of your business, including its mission, goals, and key financial projections.
- Market Analysis: A thorough understanding of your target market, including their demographics, needs, and competitive landscape.
- Operations Plan: A detailed description of your business operations, including production, marketing, and customer service.
- Financial Plan: A detailed financial projection, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
li>Management Team: A description of your management team’s experience, skills, and responsibilities.
Conducting Market Research and Financial Projections, An economics class formed a company
Thorough market research is crucial for understanding your target market. Conduct surveys, focus groups, and analyze industry data to gather insights into customer needs, preferences, and competition. Financial projections, based on market research and industry trends, are essential for forecasting revenue, expenses, and profitability.
Sample Business Plan for an Economics Class
Here’s a sample business plan template tailored to an economics class:
- Executive Summary: Describe your business concept, market opportunity, and financial projections.
- Market Analysis: Analyze the target market, including demographics, needs, and competitive landscape.
- Operations Plan: Artikel your production process, marketing strategy, and customer service approach.
- Management Team: Describe the skills and experience of your management team.
- Financial Plan: Project revenue, expenses, and profitability using industry data and market research.
Funding and Capitalization
Securing funding is crucial for student-led companies to transform their business ideas into reality. Various financing options are available, each with its advantages and disadvantages. This section will delve into the funding landscape, providing guidance on choosing the most suitable option for student entrepreneurs.
An economics class at the local high school decided to form a company to learn about business firsthand. They started by selling T-shirts and quickly realized the importance of managing their accounts receivable. An aging of their accounts receivable indicated that $4000 was past due, which could have a significant impact on their cash flow.
The students learned a valuable lesson about the importance of managing their finances effectively.
Bootstrapping
Bootstrapping involves using personal savings, earnings from sales, or contributions from friends and family to fund a company. This method offers greater control and flexibility, but it may limit growth potential due to capital constraints.
Crowdfunding
Crowdfunding platforms like Kickstarter and GoFundMe allow companies to raise funds from a large number of individuals. This method can generate significant capital and create a buzz around the company, but it may involve giving up equity or facing intense competition.
Angel Investors
Angel investors are individuals with high net worth who provide seed funding to early-stage companies in exchange for equity. They offer mentorship and expertise but typically expect high returns on investment.
Venture Capitalists
Venture capitalists are investment firms that provide funding to high-growth potential companies. They offer larger sums of capital than angel investors but also take a more active role in the company’s management.
Case Studies
- University of California, Berkeley:The student-led company, Lime, secured $335 million in venture capital funding to develop its electric scooter sharing service.
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology:The student-led company, Moderna, raised over $1 billion through an initial public offering to fund its mRNA vaccine research.
Product or Service Development
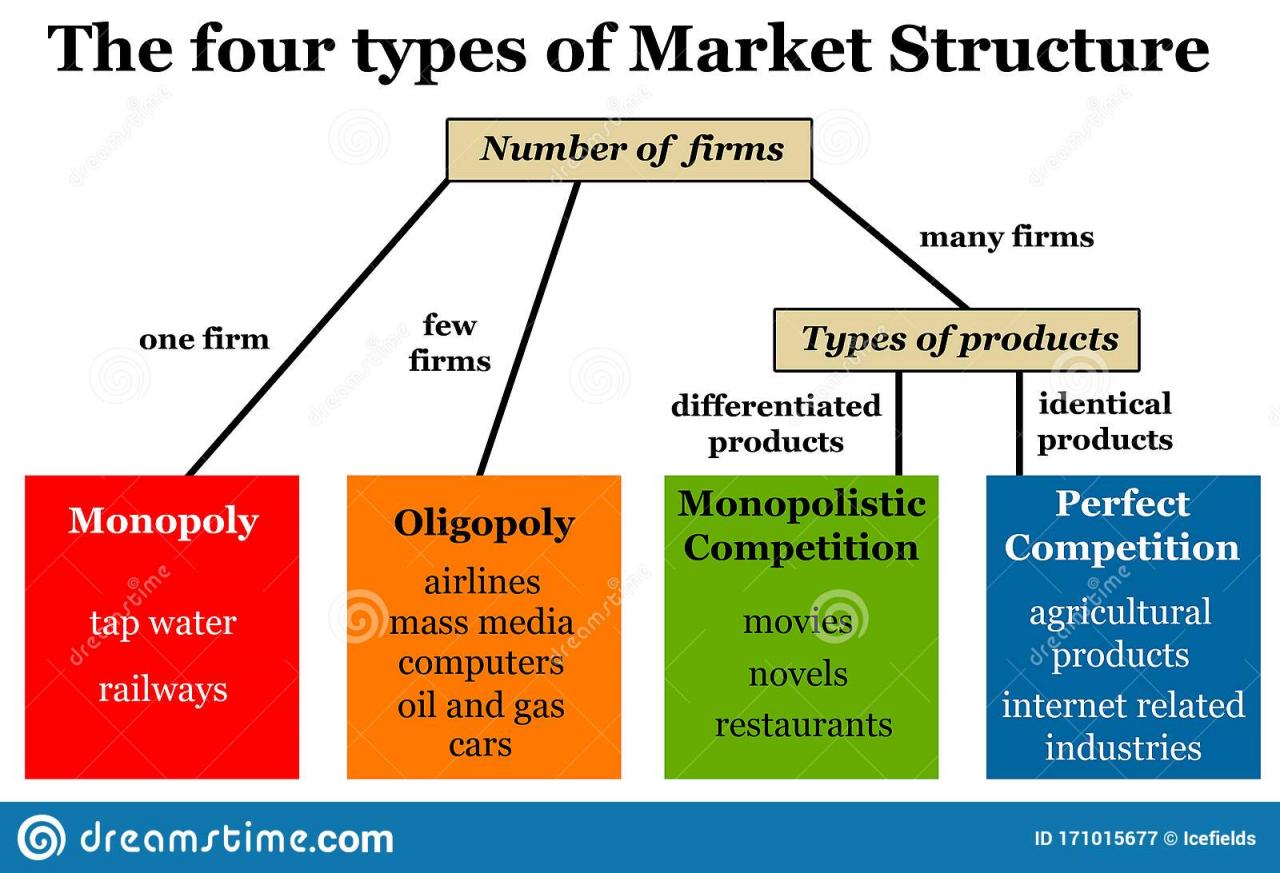
Developing a product or service involves identifying a market need, designing a solution, and creating a plan for bringing it to market. This process requires creativity, research, and careful planning.One of the most important aspects of product or service development is customer validation.
This involves getting feedback from potential customers to ensure that your product or service meets their needs and solves their problems. Customer validation can be done through surveys, interviews, and focus groups.
Innovative Products or Services Created by Economics Classes
Economics classes have created a number of innovative products and services, including:
- A mobile app that helps users track their spending and make better financial decisions.
- A website that provides personalized financial advice to users based on their income, spending habits, and goals.
- A software program that helps businesses optimize their pricing strategies.
These products and services have all been developed to meet a specific market need, and they have all been successful in attracting customers.
Marketing and Sales

Marketing and sales are crucial aspects of any business, including those formed by economics classes. Marketing involves identifying and targeting potential customers, creating awareness, and promoting products or services. Sales involve the actual transaction and exchange of goods or services for monetary compensation.
There are various marketing channels available, including online platforms (e.g., social media, search engines), traditional channels (e.g., print advertising, billboards), and word-of-mouth marketing. Sales strategies may include direct sales, online sales, or partnerships with distributors.
Who would’ve thought that an economics class could spawn a real-life business venture? These enterprising students pooled their knowledge and resources to establish an an auto insurance company . Their innovative approach to risk assessment and customer service has made them a formidable player in the industry, proving that classroom theories can translate into tangible success in the real world.
Case Studies
Several economics classes have successfully marketed and sold their products or services. For instance, students at the University of California, Berkeley, developed a subscription box service featuring locally sourced produce and sustainable products. They used social media and community outreach to market their service, highlighting the ethical and environmental benefits.
An economics class took their learning to the next level by forming their own company. With their newfound business acumen, they were able to navigate the complexities of the market. They even mastered the art of video conferencing, using Zoom to connect with clients and investors.
If you’re curious about using Zoom on an Android device, here’s a helpful guide . The company’s success is a testament to the power of education and the entrepreneurial spirit that drives our economy.
Another example is a group of students at Stanford University who created a consulting service that provided financial advice to small businesses. They leveraged their academic knowledge and networking opportunities to reach potential clients, and their service gained recognition for its practical and cost-effective solutions.
Operations and Management
The operations and management of a company are crucial for its success. They encompass all the activities and processes involved in running the business, from production and inventory management to marketing and sales. Efficient operations and effective leadership are essential for any company to achieve its goals.
Key Aspects of Business Operations and Management
- Production and inventory management
- Marketing and sales
- Customer service
- Human resources
- Finance and accounting
Importance of Efficient Operations and Effective Leadership
Efficient operations and effective leadership are essential for any company to achieve its goals. Efficient operations allow a company to produce goods or services at a low cost and with high quality. Effective leadership provides the vision and direction necessary to motivate employees and achieve success.
Examples of How Economics Classes Have Managed Their Companies Successfully
- The University of Michigan’s student-run investment fund, the Michigan Student Investment Fund, has consistently outperformed the market.
- The University of California, Berkeley’s student-run consulting firm, the Berkeley Consulting Group, has been ranked among the top consulting firms in the country.
- The Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s student-run technology incubator, the Martin Trust Center for MIT Entrepreneurship, has helped launch over 100 successful startups.
Financial Management

Financial management is the process of planning, organizing, controlling, and monitoring financial resources to achieve an organization’s objectives. It involves activities such as budgeting, cash flow management, and profitability analysis.
Budgeting is the process of creating a plan for how an organization will spend its money. A budget helps to ensure that the organization has the resources it needs to achieve its goals and that it is spending its money wisely.
Cash flow management is the process of managing the flow of money into and out of an organization. It is important to ensure that the organization has enough cash to meet its obligations and that it is using its cash efficiently.
Yo, check this out! An economics class got together and started their own company. They’re all about that green, man. And guess what? They hooked up with this company that has an ecommerce checkout workflow that writes . That’s right, it writes! So, their company is like, totally crushing it in the online biz.
Profitability analysis is the process of measuring an organization’s profitability. It helps to ensure that the organization is making enough money to cover its costs and that it is generating a profit.
Examples of How Economics Classes Have Managed Their Finances Effectively
- One economics class created a budget that allowed them to purchase the necessary supplies for their class projects while staying within their budget.
- Another economics class managed their cash flow effectively by tracking their expenses and income and by making sure that they had enough cash on hand to meet their obligations.
- A third economics class conducted a profitability analysis that helped them to identify ways to increase their revenue and reduce their costs.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Businesses are subject to a myriad of legal and regulatory requirements, designed to protect consumers, employees, and the environment. Understanding and complying with these requirements is essential for business success.
An economics class formed a company and guess what? It’s thriving! The students learned about supply and demand, marketing, and finance, and they put their knowledge to work. They created a product that people wanted, and they marketed it effectively.
They even managed to get their product into stores. Meanwhile, an automobile company shuts down a factory . But our economics class company is still going strong. They’re a testament to the power of education and entrepreneurship.
One of the most important aspects of legal and regulatory compliance is intellectual property protection. Intellectual property refers to creations of the mind, such as inventions, literary and artistic works, and trademarks. Protecting intellectual property rights is essential for businesses to safeguard their innovations and investments.
Intellectual Property Protection
- Patents protect inventions for a period of 20 years, providing exclusive rights to the inventor to make, use, sell, or license the invention.
- Copyrights protect original works of authorship, such as books, music, and artwork, for the lifetime of the author plus 70 years.
- Trademarks protect distinctive signs, such as brand names and logos, from unauthorized use by competitors.
Compliance in Economics Classes
Economics classes often incorporate hands-on projects that require students to navigate legal and regulatory issues. For example, students may be tasked with starting a small business and must comply with all applicable laws and regulations.
Through these projects, students learn the importance of understanding and complying with legal requirements, and develop skills in researching and applying relevant laws and regulations to business decision-making.
Social Impact and Sustainability: An Economics Class Formed A Company
In today’s business landscape, it’s not enough to simply maximize profits. Companies are increasingly expected to make a positive impact on society and the environment. This is where social impact and sustainability come into play.
Social impact refers to the positive or negative effects a company has on its stakeholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, and the community. Sustainability refers to the ability of a company to operate in a way that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
There are many ways that economics classes can incorporate these principles into their companies. One way is to focus on creating products or services that have a positive social impact. For example, a company could develop a product that helps people save energy or reduce their carbon footprint.
Another way to incorporate social impact and sustainability is to adopt responsible business practices. This could include paying fair wages, sourcing materials from sustainable suppliers, and reducing waste.
There are many examples of economics classes that have made a positive social or environmental impact. One example is the student-run company TOMS Shoes. TOMS Shoes sells shoes that are made from sustainable materials and donates a pair of shoes to a child in need for every pair of shoes sold.
Another example is the student-run company Green Mountain Energy. Green Mountain Energy sells renewable energy and has invested in projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
These are just a few examples of how economics classes can make a positive impact on society and the environment. By incorporating social impact and sustainability into their companies, economics classes can help create a more just and sustainable world.
Examples of Social Impact and Sustainability Initiatives
- Developing a product that helps people save energy or reduce their carbon footprint
- Adopting responsible business practices, such as paying fair wages, sourcing materials from sustainable suppliers, and reducing waste
- Donating a portion of profits to charity
- Investing in projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions
- Creating a company culture that values social responsibility and sustainability
Final Conclusion
As their company flourished, the economics class left an indelible mark on the business landscape. They demonstrated the transformative power of education, proving that students can not only learn about business but also actively participate in its creation. Their legacy serves as an inspiration to future generations of students, encouraging them to embrace the entrepreneurial spirit and make a meaningful impact on the world.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the benefits of an economics class forming a company?
An economics class forming a company provides students with hands-on experience in business operations, fosters creativity and innovation, and enhances their understanding of economic principles.
What are the challenges faced by an economics class forming a company?
Challenges include balancing academic responsibilities with business operations, securing funding, navigating legal and regulatory requirements, and managing the dynamics of a student-led team.
How can an economics class ensure the success of their company?
Keys to success include developing a solid business plan, conducting thorough market research, securing adequate funding, building a strong team, and adapting to market changes.