In today’s competitive business landscape, data is king, and sales data is no exception. An employee compiled sales data can provide businesses with a wealth of insights into their sales performance, helping them identify areas for improvement and drive growth.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the methods, techniques, and best practices for effectively compiling, analyzing, and utilizing sales data to maximize sales performance.
From data collection and analysis to visualization and interpretation, we will explore the entire sales data management process. Whether you’re a sales manager looking to improve your team’s performance or a business owner seeking to gain a competitive edge, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools you need to harness the power of sales data.
Data Collection Methods
Gathering sales data is essential for businesses to understand customer behavior, optimize strategies, and make informed decisions. Various methods are employed to collect this data, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
The most common methods include surveys, interviews, and observation.
After an employee compiled sales data, management took note and decided to act. In a response to an employee’s idea , management outlined plans to use the data to improve sales strategies and increase revenue. The employee’s contribution was recognized and appreciated, demonstrating the value of employee feedback in driving business success.
Surveys
Surveys are a popular method for collecting data from a large number of people. They can be conducted online, via email, or in person.
- Advantages:Surveys are relatively inexpensive and easy to conduct. They can reach a large audience and provide quantitative data that can be analyzed statistically.
- Disadvantages:Surveys can be biased if the sample is not representative of the population. Response rates can be low, and respondents may not provide accurate or complete information.
Interviews
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals one-on-one. They can be conducted in person, over the phone, or via video conference.
- Advantages:Interviews allow for more in-depth exploration of customer experiences and motivations. They can provide qualitative data that can be used to generate insights and hypotheses.
- Disadvantages:Interviews are more time-consuming and expensive than surveys. They can be biased if the interviewer is not objective, and respondents may be influenced by the interviewer’s presence.
Observation
Observation involves watching and recording customer behavior in a natural setting. This can be done in person or through video surveillance.
Yo, check it out! An employee was busy as a bee, crunching numbers and compiling sales data like a boss. But hold up, relationships at work are like a dance – you gotta know your role. What’s the deal between an employee and a supervisor ? It’s like a partnership, where the supervisor’s got the moves and the employee’s got the hustle.
Back to our data-crunching employee, armed with their newfound knowledge, they’re ready to slay those sales goals!
- Advantages:Observation provides objective data on customer behavior. It can be used to identify patterns and trends that may not be apparent from surveys or interviews.
- Disadvantages:Observation can be time-consuming and expensive. It can also be difficult to observe customer behavior in a natural setting without influencing it.
Data Analysis Techniques
The collected sales data can be analyzed using a variety of statistical techniques to identify trends, patterns, and relationships. These techniques help businesses gain insights into their sales performance, customer behavior, and market dynamics.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a statistical technique used to determine the relationship between a dependent variable (e.g., sales) and one or more independent variables (e.g., advertising expenditure, price). It allows businesses to predict future sales based on changes in the independent variables.
An employee meticulously compiled sales data, demonstrating a keen eye for detail and analytical prowess. Employers seek individuals who possess these qualities, along with others outlined in 10 top characteristics employers look for in an employee . These traits, including teamwork and communication skills, are essential for success in any role.
By honing these attributes, employees can enhance their value to their organizations and excel in their careers.
Correlation Analysis
Correlation analysis measures the strength and direction of the relationship between two or more variables. It helps businesses identify variables that are highly correlated with sales, such as customer demographics, product features, or marketing campaigns.
An employee compiled sales data to provide insights for better decision-making. Often, a transfer offers an employee new opportunities for growth and development. This employee’s transfer to a different department allowed them to apply their data analysis skills in a new context, further enhancing their expertise in sales data analysis.
Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis is a statistical technique used to analyze data collected over time. It helps businesses identify trends, seasonality, and other patterns in their sales data. This information can be used to forecast future sales and plan for inventory, staffing, and marketing.
Data Visualization
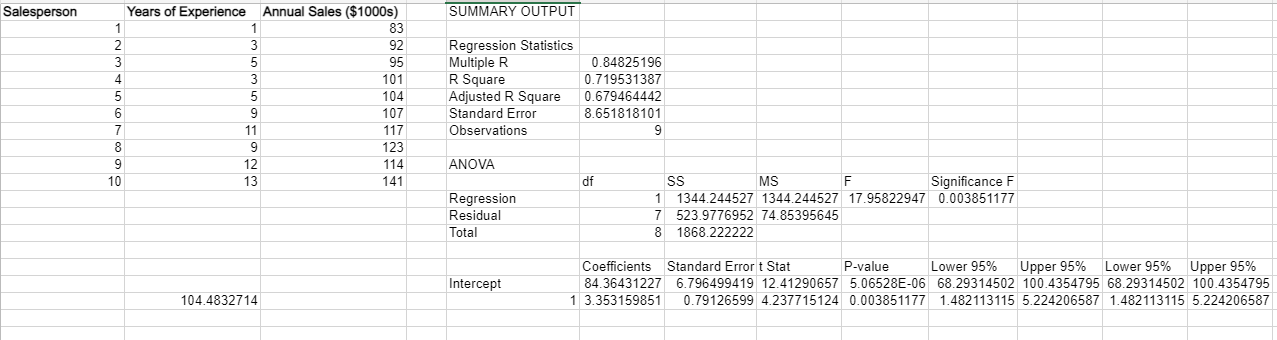
Data visualization is crucial for presenting sales data as it transforms complex data into visual representations, making it easier to understand and draw insights. It helps identify trends, patterns, and relationships within the data, enabling informed decision-making.
Effective Data Visualization Techniques
Effective data visualization techniques include:
- Charts:Charts, such as bar charts, line charts, and pie charts, provide a clear and concise way to compare data points and identify trends.
- Graphs:Graphs, such as scatterplots and histograms, allow for more complex data exploration and identifying correlations and distributions.
- Tables:Tables present data in a structured format, making it easy to compare specific data points and identify outliers.
Data Interpretation
Interpreting data analysis results involves identifying patterns, trends, and insights that can inform business decisions. By examining the data and drawing meaningful conclusions, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of customer behavior, market trends, and sales performance.
An employee diligently compiled sales data, meticulously recording each transaction. As they delved deeper into their work, they stumbled upon a crucial question: should they file as a 1099 contractor or an employee? Seeking guidance, they consulted 1099 as an employee , a comprehensive resource that illuminated the intricacies of employment classification.
Armed with newfound knowledge, they continued their data analysis, confident in their understanding of the complexities surrounding employee compensation.
Identifying Trends and Patterns
- Time-series analysis:Tracking data over time to identify patterns and trends. For example, analyzing sales data by month to identify seasonal fluctuations or growth trends.
- Correlation analysis:Examining the relationship between two or more variables. For example, correlating sales data with marketing spend to determine the impact of marketing campaigns.
Extracting Insights
Once trends and patterns are identified, businesses can extract insights that drive decision-making.
When an employee compiled sales data, it’s a good idea to have a write up for an employee on file. This will help you keep track of their progress and make sure they’re meeting expectations. The write-up should include information about the employee’s sales goals, performance, and any other relevant information.
It’s also a good idea to have the employee sign the write-up so that they’re aware of its contents.
- Identify opportunities:Data interpretation can reveal areas where sales performance can be improved. For example, identifying underperforming products or regions.
- Optimize strategies:Insights can guide sales teams in optimizing their strategies. For example, adjusting marketing campaigns based on customer preferences or targeting specific customer segments.
- Forecast future performance:Data analysis can help businesses forecast future sales performance by identifying trends and predicting market behavior.
Example: Improving Sales Performance
A sales team analyzed their data and identified a trend: customers who purchased product A were more likely to also purchase product B. This insight led to a targeted marketing campaign that bundled the two products together, resulting in a significant increase in sales for both products.
Data Management
Sales data management involves organizing, securing, and making data accessible to authorized users. Best practices include proper data storage, security measures, and accessibility protocols.
Data governance ensures data quality, consistency, and compliance with regulations. It establishes policies and procedures for data collection, usage, and disposal.
After an employee diligently compiled the sales data, they were entitled to the 5 rights of an employee , including fair compensation and a safe working environment. With these rights in mind, the employee confidently submitted the data, knowing that their contributions would be recognized and valued.
Data Storage, An employee compiled sales data
- Use a centralized database or data warehouse for efficient storage and retrieval.
- Implement data backup and recovery systems to protect against data loss.
- Consider cloud-based storage for scalability and cost-effectiveness.
Data Security
- Implement access controls and authentication mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access.
- Encrypt sensitive data to protect it from breaches.
- Monitor data usage and access logs for suspicious activity.
Data Accessibility
- Provide authorized users with appropriate access levels based on their roles.
- Use data visualization tools to make data easily understandable and actionable.
- Establish clear data access policies and procedures.
Data Governance
- Establish data ownership and accountability to ensure data integrity.
- Define data standards and guidelines to maintain data consistency.
- Implement data validation and verification processes to ensure data accuracy.
Data Quality
- Regularly monitor data for completeness, accuracy, and consistency.
- Implement data cleansing and correction processes to address data errors.
- Use data profiling tools to identify data anomalies and improve data quality.
Data Integration
Integrating sales data with other data sources can provide a more comprehensive view of customer behavior and business performance. Customer relationship management (CRM) systems store data on customer interactions, while enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems track data on business operations.
By integrating sales data with these systems, businesses can gain insights into how customers interact with their products and services, and how sales performance impacts overall business outcomes.
The employee diligently compiled the sales data, ensuring accuracy for the company’s financial records. Incidentally, have you heard about the notary who is an employee of a bank ? It’s a fascinating role that combines legal expertise with banking operations.
Returning to the employee’s task, the compiled sales data will provide valuable insights for strategic decision-making.
Benefits of Data Integration
- Improved customer insights: By combining sales data with customer data, businesses can gain a better understanding of customer needs, preferences, and buying habits.
- Enhanced sales forecasting: By integrating sales data with data on customer interactions and business operations, businesses can improve the accuracy of their sales forecasts.
- Optimized marketing campaigns: By understanding which customers are most likely to purchase certain products or services, businesses can tailor their marketing campaigns to target the right audience.
- Improved operational efficiency: By integrating sales data with data on business operations, businesses can identify areas where they can improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Challenges of Data Integration
- Data quality: Data quality is a major challenge in data integration. Data from different sources may be inconsistent, incomplete, or inaccurate.
- Data security: Data security is another important consideration in data integration. Businesses need to ensure that customer data is protected from unauthorized access.
- Technical complexity: Data integration can be a complex technical process. Businesses need to have the right tools and expertise to successfully integrate data from different sources.
Data Mining
Data mining is the process of extracting hidden patterns and insights from large datasets. In the sales context, data mining can be used to identify trends, customer preferences, and other valuable information that can help businesses improve their sales strategies.
Techniques Used in Data Mining
There are a variety of data mining techniques that can be used to analyze sales data, including:
- Association analysis: This technique identifies relationships between different items or events. For example, a retailer might use association analysis to identify which products are frequently purchased together.
- Clustering: This technique groups similar data points together. For example, a sales manager might use clustering to identify different customer segments based on their purchase history.
- Classification: This technique predicts the value of a target variable based on a set of input variables. For example, a sales team might use classification to predict which customers are most likely to make a purchase.
Applications of Data Mining in Sales
Data mining has a wide range of applications in the sales context, including:
- Customer segmentation: Data mining can be used to identify different customer segments based on their demographics, purchase history, and other factors. This information can be used to target marketing campaigns and sales efforts.
- Product recommendations: Data mining can be used to identify products that customers are likely to be interested in based on their past purchases. This information can be used to personalize product recommendations and increase sales.
- Fraud detection: Data mining can be used to identify fraudulent transactions by analyzing patterns in customer behavior. This information can be used to prevent fraud and protect businesses from financial losses.
Machine Learning
Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed. This makes it an ideal tool for automating sales data analysis and forecasting.
Machine learning algorithms can be used to identify patterns and trends in sales data, which can then be used to make predictions about future sales. This information can be used to make better decisions about pricing, marketing, and inventory management.
Machine Learning Algorithms Used in Sales
- Linear regression: This algorithm is used to predict a continuous value, such as sales revenue, based on a set of independent variables, such as advertising spending.
- Logistic regression: This algorithm is used to predict a binary outcome, such as whether or not a customer will make a purchase, based on a set of independent variables.
- Decision trees: This algorithm is used to create a tree-like structure that can be used to make predictions about a target variable, such as sales volume.
- Neural networks: This algorithm is used to create a complex network of nodes that can be used to learn patterns in data and make predictions.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly important role in sales data analysis. AI can be used to automate tasks, such as data cleaning and analysis, and to identify patterns and trends in data that would be difficult or impossible for humans to find.
There are a number of different ways that AI can be used in sales data analysis. One common application is chatbots and virtual assistants. These AI-powered tools can be used to answer customer questions, schedule appointments, and even close deals.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
Chatbots and virtual assistants are AI-powered tools that can be used to automate a variety of tasks, such as answering customer questions, scheduling appointments, and even closing deals. These tools can be used to improve customer service, increase sales, and reduce costs.
- Chatbots can be used to answer customer questions 24/7, even when sales reps are not available.
- Virtual assistants can be used to schedule appointments and meetings, freeing up sales reps to focus on more important tasks.
- AI-powered tools can be used to close deals by providing customers with personalized recommendations and offers.
Ethical Considerations
The analysis of sales data involves a significant responsibility to handle data ethically and responsibly. Ethical considerations encompass data privacy, data security, and responsible data handling practices to protect individuals’ rights and maintain trust.
Organizations must adhere to data protection regulations and industry best practices to safeguard sensitive information. This includes implementing robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and misuse. Additionally, obtaining informed consent from individuals before collecting and using their data is crucial to respect their privacy rights.
Data Privacy
- Comply with data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
- Obtain informed consent from individuals before collecting and using their personal data.
- Implement data minimization practices to collect only the necessary data for specific purposes.
Data Security
- Establish robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
- Train employees on data security best practices to prevent human error and malicious attacks.
- Develop incident response plans to address data breaches promptly and effectively.
Responsible Data Handling Practices
- Use data for legitimate purposes and avoid exploiting it for unfair advantage.
- Be transparent about data collection and usage practices, providing clear privacy policies.
- Allow individuals to access, correct, or delete their personal data upon request.
Best Practices: An Employee Compiled Sales Data

Effective sales data analysis is crucial for making informed decisions and driving business growth. Here are some best practices to follow:
Data Collection:
- Determine the specific business objectives you want to achieve.
- Identify the relevant data sources and collect data from multiple channels to get a comprehensive view.
- Ensure data accuracy and completeness by implementing data validation processes.
Data Analysis:
- Use appropriate analytical techniques to extract meaningful insights from the data.
- Apply statistical methods, such as regression analysis and hypothesis testing, to identify trends and patterns.
- Consider using data mining techniques to uncover hidden relationships and insights.
Data Interpretation:
Yo, an employee busted their hump compiling all that sales data. Gotta make sure they get their dough for the work they put in. The amount of money paid to an employee for work performed should be fair and square, right? That’s how we keep the team motivated and the sales rolling in.
Plus, it’s the right thing to do.
- Interpret the results of the analysis objectively and avoid making assumptions.
- Identify actionable insights that can be implemented to improve sales performance.
- Communicate the findings clearly and concisely to stakeholders.
Data Visualization:
- Use data visualization tools to present the data in an easy-to-understand format.
- Choose appropriate charts and graphs to effectively convey the key insights.
- Use color, labels, and annotations to make the visualizations visually appealing and informative.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, an employee compiled sales data is an invaluable asset for businesses looking to optimize their sales performance. By following the best practices Artikeld in this guide, businesses can effectively collect, analyze, and interpret sales data to gain actionable insights that drive growth.
Remember, data is only as valuable as the actions taken upon it, so embrace the power of sales data and unlock the full potential of your sales team.
FAQ Compilation
What are the benefits of using an employee compiled sales data?
An employee compiled sales data provides numerous benefits, including improved sales forecasting, targeted marketing campaigns, optimized pricing strategies, enhanced customer relationship management, and increased sales productivity.
How can I ensure the accuracy and reliability of my sales data?
To ensure data accuracy and reliability, implement data validation processes, conduct regular data audits, and train employees on proper data entry procedures.
What are some common challenges associated with sales data analysis?
Common challenges include data inconsistency, data volume, data integration, data security, and the need for skilled data analysts.