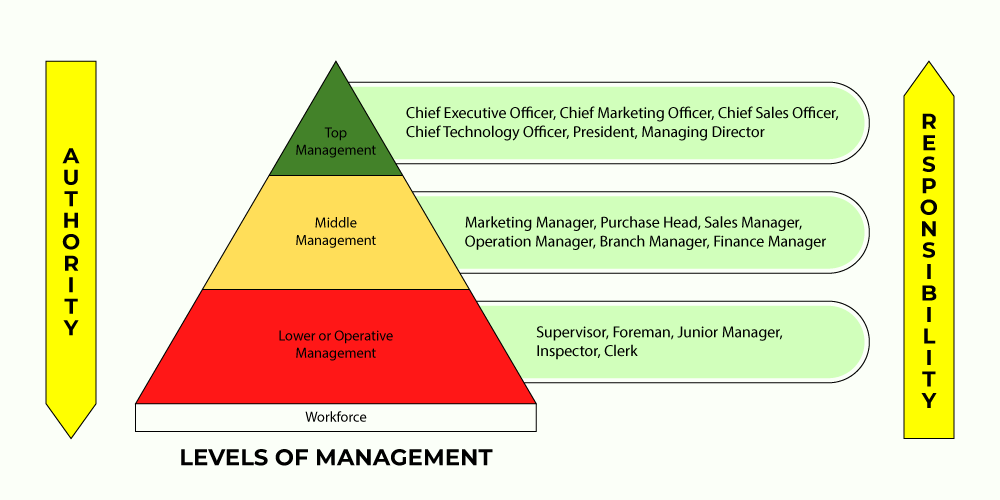
Different Levels of Management in an Organization
Different levels of management in an organization – An organization’s management structure typically comprises multiple levels, each with distinct roles and responsibilities. These levels are:
Top Management
- Chief Executive Officer (CEO)
- Chief Operating Officer (COO)
- Chief Financial Officer (CFO)
Middle Management
- Department Managers
- Project Managers
- Team Leaders
First-Line Management
- Supervisors
- Foremen
- Shift Managers
Hierarchy and Reporting Structure
An organizational chart depicts the hierarchy and reporting structure within an organization, clarifying the flow of communication and decision-making.
Different levels of management within an organization require varying skills. Managers must possess a combination of hard and soft skills to be effective in their roles. For a comprehensive understanding of these essential qualities, refer to our in-depth guide: define the skills you need to be an effective manager.
The different levels of management in an organization demand specific combinations of these skills, ensuring the smooth functioning and success of the organization.
Advantages of Different Reporting Structures
- Centralized:Clear lines of authority, efficient decision-making
- Decentralized:Empowerment of lower-level managers, faster decision-making
- Matrix:Flexibility, expertise-based decision-making
Disadvantages of Different Reporting Structures
- Centralized:Slow decision-making, lack of autonomy
- Decentralized:Potential for conflicting decisions, reduced coordination
- Matrix:Complexity, potential for confusion
Management Styles and Their Impact
Management style significantly influences employee motivation, productivity, and organizational culture.
Different levels of management in an organization play a crucial role in implementing and overseeing risk management strategies. From the board of directors, which sets the risk appetite and provides oversight, to middle managers who identify and assess risks, each level has a specific responsibility.
Understanding these responsibilities is essential for effective risk management. However, risk management in the insurance industry presents unique challenges. Describe risk management in an insurance industry to learn more about the specific risks faced by insurers and how they are managed.
Autocratic Style
- Top-down decision-making
- Limited employee input
- Can lead to employee dissatisfaction
Democratic Style, Different levels of management in an organization
- Involves employees in decision-making
- Fosters employee engagement and ownership
- Can be time-consuming
Laissez-Faire Style
- Minimal manager involvement
- Employees have significant autonomy
- Can lead to lack of direction and coordination
Leadership and Management: Different Levels Of Management In An Organization
While related, leadership and management are distinct roles.
In an organization, different levels of management hold distinct responsibilities. Assertive managers, for instance, are crucial at all levels. Their characteristics , such as clear communication, empathy, and a balanced approach to decision-making, contribute to effective team dynamics and organizational success.
Understanding the characteristics of assertive managers helps organizations identify and nurture these essential leaders at various levels of management.
Leadership
- Inspires and motivates employees
- Sets the vision and direction
- Creates a positive work environment
Management
- Plans, organizes, and controls resources
- Ensures efficient operations
- Delegates responsibilities
Span of Control
Span of control refers to the number of employees reporting to a manager. It impacts organizational efficiency.
In an organization, different levels of management play a crucial role in achieving organizational goals. From top-level executives to first-line supervisors, each level has specific responsibilities that contribute to the overall success of the company. For more insights on the role of management in an organization, refer to the comprehensive guide at describe the role of management in an organization.
Understanding the different levels of management and their respective roles is essential for effective organizational structure and performance.
Factors Influencing Span of Control
- Manager’s capabilities
- Employee experience and skills
- Task complexity
Recommendations for Optimizing Span of Control
- Consider the manager’s ability to effectively supervise
- Balance task complexity and employee skills
- Use technology to enhance communication and coordination
Decentralization and Delegation
Decentralization and delegation involve empowering managers and employees with decision-making authority.
Different levels of management within an organization have varying responsibilities in developing and implementing effective crisis management plans. These plans typically include elements such as identifying potential risks, establishing response protocols, and coordinating communication strategies. By understanding the elements of an effective crisis management plan , managers can ensure that their organizations are well-prepared to respond to unexpected events and mitigate their impact on operations and reputation.
Benefits of Decentralization and Delegation
- Faster decision-making
- Increased employee autonomy and motivation
- Improved organizational agility
Challenges of Decentralization and Delegation
- Potential for inconsistent decision-making
- Lack of coordination and control
- Increased manager workload
Best Practices for Effective Delegation
- Clearly define roles and responsibilities
- Provide adequate training and support
- Monitor progress and provide feedback
Final Summary
In conclusion, different levels of management are essential for maintaining order, accountability, and effective decision-making within an organization. By understanding the roles, responsibilities, and reporting structures at each level, organizations can optimize their management systems and create a positive and productive work environment.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the primary levels of management in an organization?
Top-level management (executives), middle management (department heads), and frontline management (supervisors)
How does the span of control impact management effectiveness?
In any organization, different levels of management are essential for effective decision-making and execution. These levels, from front-line supervisors to senior executives, play distinct roles in setting and achieving organizational goals. To optimize their effectiveness, managers at all levels must have a strong understanding of program design and management principles.
Designing and Managing Programs: An Effectiveness-Based Approach provides a comprehensive framework for managers to enhance their program development and implementation skills, ultimately contributing to the success of their organizations and the different levels of management within them.
A wider span of control can increase efficiency but may also reduce employee supervision and support.
What are the benefits of decentralization and delegation?
Empowers lower-level managers, improves decision-making speed, and fosters employee development.
In any organization, there are different levels of management, each with its own responsibilities and scope of authority. The top level of management, typically the CEO and board of directors, is responsible for setting the overall direction and strategy of the organization.
Middle management is responsible for implementing the plans and policies set by top management and for managing the day-to-day operations of the organization. First-line management is responsible for supervising the work of employees and for ensuring that the organization’s goals are met.
Just as different levels of management have different responsibilities, so too do different types of investment managers. When choosing an investment manager , it is important to consider the level of management that is appropriate for your needs. If you are a large organization with complex investment needs, you may need a top-level investment manager.
If you are a smaller organization with less complex investment needs, a middle-level or first-line investment manager may be more appropriate.
Management roles in an organization vary widely in scope and responsibility, from frontline supervisors to top-level executives. The same principle applies in healthcare, where different levels of management, including primary care physicians, specialists, and hospital administrators, work together to provide comprehensive care for patients.
For instance, describe the management for an acute asthma attack involves collaboration between emergency room physicians, respiratory therapists, and nurses, each playing a crucial role in managing the patient’s condition. Similarly, in an organization, effective collaboration among different levels of management ensures efficient operations and optimal outcomes.