Financial Planning and Budgeting
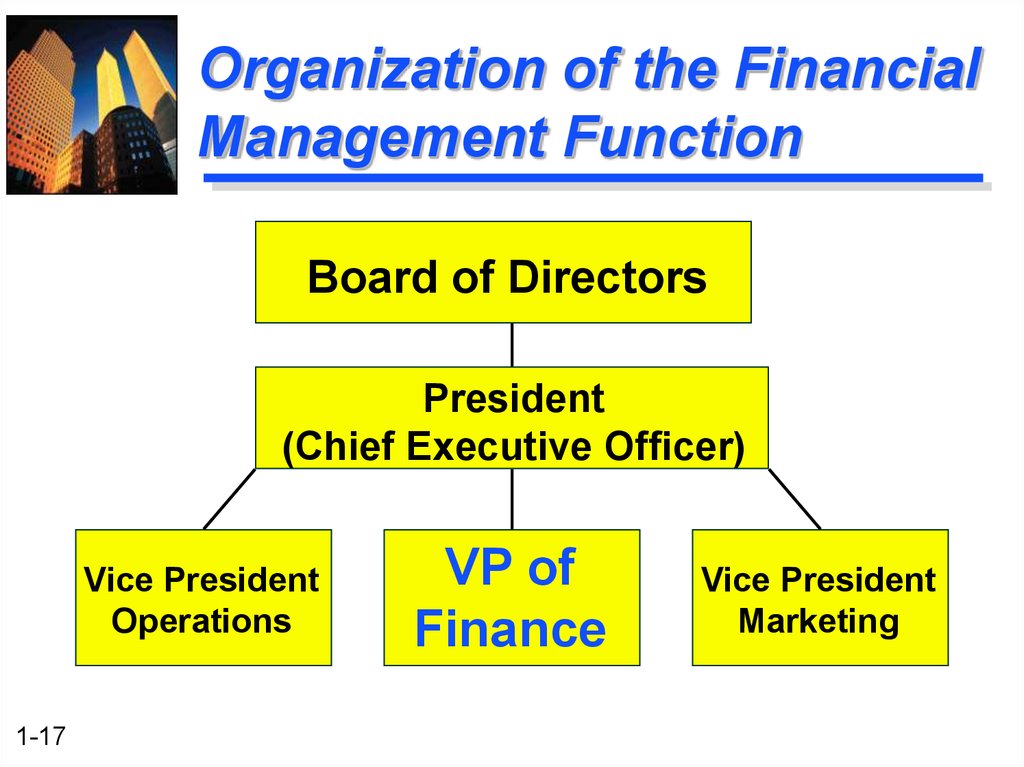
Financial management in an organization – Financial planning and budgeting are essential processes that help organizations allocate resources effectively, set financial goals, and make informed decisions. The principles of financial planning involve forecasting future financial performance, identifying potential risks and opportunities, and developing strategies to achieve desired outcomes.
Financial management is crucial for organizations to allocate resources effectively. However, when an employee experiences an acute asthma attack, prompt medical attention is essential. For instance, here’s a guide on managing such an attack. Once the employee’s health is stabilized, financial managers can resume their responsibilities, ensuring the organization’s financial well-being.
Methods used to create financial plans and budgets include scenario planning, rolling forecasts, and zero-based budgeting. Scenario planning involves developing multiple financial plans based on different assumptions about future events. Rolling forecasts are updated regularly to reflect changes in the business environment, while zero-based budgeting requires organizations to justify every expense from scratch each period.
Financial management in an organization is crucial for weathering crises. Crisis management plans should outline communication strategies, response protocols, and recovery measures to minimize disruptions. Elements of an effective crisis management plan include establishing a crisis team, identifying potential risks, developing communication channels, and securing resources.
By implementing a robust crisis management plan, organizations can safeguard their financial stability and reputation during challenging times.
Effective financial planning and budgeting practices include setting realistic goals, aligning financial plans with strategic objectives, and involving all relevant stakeholders in the process.
Cash Flow Management
Cash flow management is crucial for organizations to maintain financial stability and liquidity. It involves monitoring the flow of cash into and out of the business, and implementing strategies to optimize cash flow.
Strategies for optimizing cash flow include accelerating collections from customers, negotiating extended payment terms with suppliers, and managing inventory levels efficiently.
Potential cash flow risks include seasonality, changes in customer demand, and unexpected expenses. Mitigation plans for cash flow risks involve building up cash reserves, securing lines of credit, and implementing contingency plans.
Financial management is a critical aspect of any organization, ensuring efficient resource allocation and long-term stability. As organizations navigate the complexities of long-term care management, they can benefit from insights provided in Dimensions of Long Term Care Management: An Introduction, 2nd Edition.
This comprehensive resource offers guidance on strategic planning, financial forecasting, and risk management, ultimately enhancing the organization’s financial health and ability to provide quality care.
Investment and Capital Management
Investment and capital management involve making decisions about how to allocate financial resources to maximize returns and support the organization’s strategic objectives.
In the realm of financial management within an organization, effective management practices are crucial for success. Just as classroom management fosters a conducive environment for student learning, so too does financial management establish a framework for prudent decision-making and resource allocation, ensuring the organization’s long-term financial health.
Different investment strategies include investing in stocks, bonds, real estate, and alternative assets. The potential returns of these investments vary depending on factors such as risk tolerance, time horizon, and market conditions.
Capital budgeting involves evaluating and selecting long-term investment projects. The goal of capital budgeting is to allocate capital to projects that will generate the highest returns for the organization.
Financial management is a critical aspect of any organization, ensuring efficient and effective handling of financial resources. The advancement of technology has introduced innovative solutions such as embedded computers, which have found applications in various domains, including financial transactions. Can an embedded computer manage financial transactions at an ATM ?
Exploring the capabilities of embedded computers in financial management can provide valuable insights for organizations seeking to optimize their financial operations.
Financial Risk Management
Financial risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating financial risks that could impact the organization’s financial performance and stability.
Financial management is essential for any organization to ensure its financial health and stability. One key aspect of financial management is risk management, which involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks that could impact the organization’s financial performance. Commercial banks, in particular, face unique risks due to their role as financial intermediaries, including credit risk, market risk, and operational risk.
Understanding and managing these risks is crucial for commercial banks to maintain their solvency and profitability. Commercial bank risk management: an analysis of the process provides a comprehensive analysis of risk management practices in commercial banks, offering valuable insights for financial managers and risk professionals.
Methods for mitigating and managing financial risks include hedging, diversification, and insurance. Hedging involves using financial instruments to reduce the impact of price fluctuations. Diversification involves investing in a variety of assets to reduce the overall risk of the portfolio.
Insurance can be used to transfer the risk of specific events to an insurance company.
Best practices for implementing a comprehensive risk management framework include conducting regular risk assessments, establishing risk tolerance limits, and developing contingency plans for potential risks.
Performance Measurement and Reporting
Performance measurement is essential for financial management as it provides insights into the financial health and performance of the organization.
Financial management in an organization is crucial for ensuring the efficient allocation of resources. It involves planning, budgeting, and controlling the financial activities of an organization. Effective financial management can lead to increased profitability, reduced costs, and improved cash flow.
However, change management can significantly impact financial management, as it may require organizations to reallocate resources, adjust budgets, and implement new financial strategies. Understanding the effects of change management in an organisation can help organizations minimize financial risks and maximize the benefits of change.
Key financial performance indicators (KPIs) include revenue, profit margin, return on assets (ROA), and return on equity (ROE). These KPIs help organizations track their progress towards financial goals and identify areas for improvement.
Financial reporting and disclosure involve communicating the organization’s financial performance to stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and regulators. Financial reports include the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement.
Financial management is crucial for organizations to maintain financial stability and growth. Effective small business management, as outlined in the article effective small business management an entrepreneurial approach , emphasizes the importance of financial planning, budgeting, and cash flow management.
By implementing these principles, organizations can optimize their financial resources and make informed decisions that contribute to their long-term success.
Financial Control and Audit
Financial control and audit are essential for ensuring the accuracy and integrity of financial information and preventing fraud and errors.
Internal control systems involve policies and procedures designed to prevent, detect, and correct errors and fraud. These systems include segregation of duties, authorization controls, and reconciliation procedures.
Financial audits are conducted by independent auditors to provide assurance on the accuracy and reliability of financial statements. Audit reports provide insights into the effectiveness of internal control systems and the overall financial health of the organization.
Emerging Trends in Financial Management, Financial management in an organization
Emerging trends in financial management include the increasing use of technology, artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics.
Technology is being used to automate financial processes, improve data analysis, and enhance risk management. AI is being used to develop predictive models and identify patterns in financial data. Data analytics is being used to gain insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operational efficiency.
Closing Summary: Financial Management In An Organization
In conclusion, financial management is a multifaceted discipline that requires a deep understanding of financial principles and a strategic mindset. By implementing sound financial management practices, organizations can enhance their financial performance, reduce risks, and position themselves for long-term success.
Essential FAQs
What is the importance of financial planning and budgeting?
Financial planning and budgeting provide a roadmap for an organization’s financial future. They help organizations allocate resources effectively, prioritize spending, and make informed decisions.
How can organizations optimize cash flow?
Optimizing cash flow involves managing inflows and outflows effectively. Strategies include improving receivables management, negotiating favorable payment terms with suppliers, and exploring financing options.
What is the role of investment and capital management?
Investment and capital management involve making decisions about how to allocate an organization’s financial resources. This includes evaluating investment opportunities, managing capital structure, and optimizing returns.
How can organizations manage financial risks?
Financial risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating financial risks. Organizations can implement risk management strategies such as diversification, hedging, and insurance to protect themselves from potential losses.
What are key financial performance indicators (KPIs)?
KPIs are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound metrics that organizations use to track their financial performance. Common KPIs include revenue growth, profit margin, and return on investment.