Revenue Streams
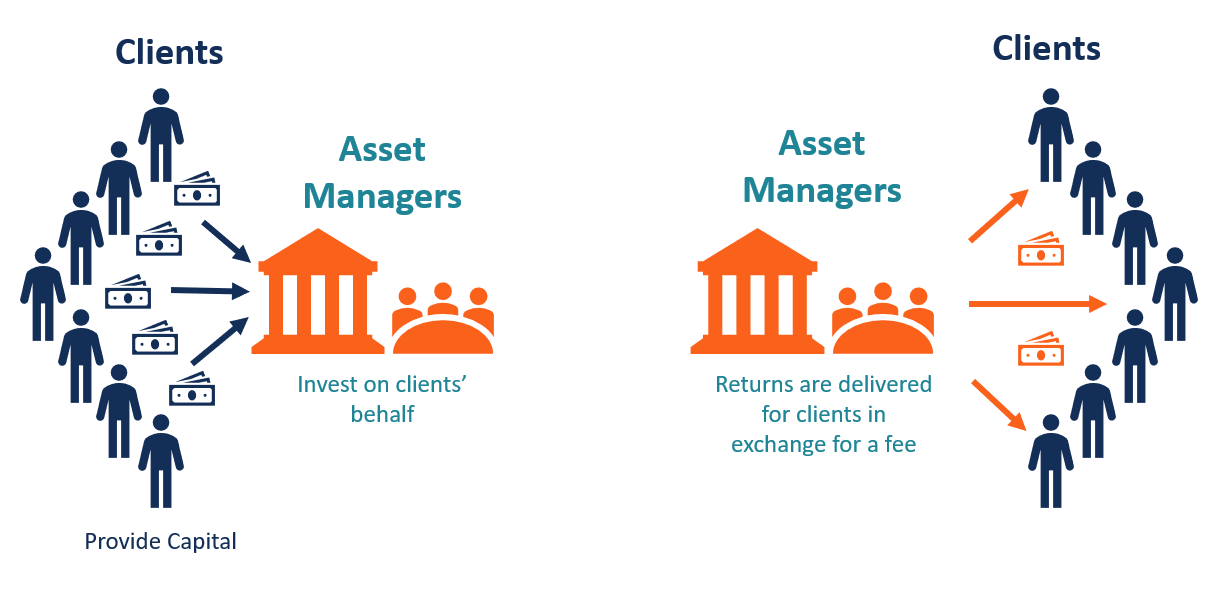
How does an asset manager make money – Asset managers generate revenue primarily through fees charged to their clients. These fees can vary depending on the type of asset managed, the investment strategy employed, and the performance of the portfolio.
Asset managers typically make money through a combination of fees, commissions, and performance-based incentives. Fees can be charged as a percentage of assets under management, while commissions are paid on trades executed on behalf of clients. Performance-based incentives reward managers for exceeding certain investment targets.
Health information management an applied approach 5th edition provides a comprehensive overview of the principles and practices of health information management, including topics such as data collection, storage, retrieval, and analysis. Understanding these concepts is essential for asset managers who need to effectively manage and analyze large datasets in order to make informed investment decisions.
- Management fees:A fixed percentage of assets under management (AUM), typically ranging from 0.25% to 2% per year.
- Performance-based fees:Contingent on the portfolio’s performance, such as a percentage of investment gains or a high-water mark that protects investors from losses.
- Transaction fees:Charged for buying or selling securities within the portfolio, usually a percentage of the transaction value.
- Other fees:May include custody fees for holding assets, advisory fees for financial planning services, and research fees for access to proprietary insights.
Investment Strategies: How Does An Asset Manager Make Money
Asset managers employ a range of investment strategies to meet the varying risk appetites and return objectives of their clients.
Asset managers generate revenue through various means, including management fees, performance fees, and commissions. They typically charge a percentage of assets under management as a management fee, and may also charge a performance fee if they exceed a certain benchmark.
Additionally, they may earn commissions on trades executed on behalf of their clients. For more information on hospital management systems, refer to draw an er diagram for hospital management system.
Active vs. Passive Management
- Active management:Involves making investment decisions with the aim of outperforming a benchmark or index.
- Passive management:Tracks a specific benchmark or index, aiming to replicate its performance with lower fees.
Growth vs. Value Investing
- Growth investing:Focuses on companies with high growth potential, often with higher valuations.
- Value investing:Seeks undervalued companies with solid fundamentals and potential for appreciation.
Portfolio Management
Portfolio management involves constructing and managing a diversified portfolio of assets to meet specific investment objectives.
Asset managers typically generate revenue through fees charged to clients for managing their investments. These fees can vary depending on the type of asset being managed, the size of the portfolio, and the level of service provided. Some asset managers also offer additional services, such as financial planning and tax advice, which can generate additional revenue streams.
By integrating elements of an environmental management system elements of an environmental management system , asset managers can improve their overall risk management and enhance their reputation with investors, which can lead to increased demand for their services and higher revenue.
Diversification
- Spreading investments across different asset classes (e.g., stocks, bonds, real estate) and sectors to reduce risk.
- Helps mitigate the impact of losses in any one asset class or sector.
Rebalancing
- Adjusting the portfolio’s asset allocation over time to maintain the desired risk-return balance.
- Ensures that the portfolio remains aligned with the investor’s goals.
Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is a critical aspect of portfolio management, determining the proportion of the portfolio invested in different asset classes.
Asset managers generate revenue primarily through fees charged to clients for managing their investments. These fees can vary depending on the type of investment strategy, asset class, and performance. Customer experience management , a critical aspect of modern business, plays a role in attracting and retaining clients, which can ultimately impact the asset manager’s revenue generation capabilities.
Factors Influencing Asset Allocation
- Investor’s risk tolerance and time horizon.
- Current economic conditions and market outlook.
- Diversification goals and return objectives.
Asset Allocation Models
- Strategic asset allocation:Long-term allocation based on the investor’s risk profile and investment goals.
- Tactical asset allocation:Short-term adjustments based on market conditions and investment opportunities.
Performance Measurement
Measuring the performance of asset managers is essential for evaluating their effectiveness and holding them accountable.
Risk-Adjusted Returns
- Sharpe ratio:Measures excess return per unit of risk taken.
- Sortino ratio:Focuses on excess return relative to downside risk.
Industry Benchmarks, How does an asset manager make money
- Peer group comparison:Comparing returns to similar asset managers with similar investment strategies.
- Index comparison:Measuring returns against a relevant market index.
Ultimate Conclusion
In the realm of asset management, revenue generation is a multifaceted endeavor that encompasses a wide range of strategies. Asset managers leverage performance-based fees, employ diverse investment strategies, and implement sophisticated portfolio management techniques to maximize returns for their clients.
Understanding these revenue-generating mechanisms is essential for investors seeking to align their financial goals with the expertise of asset managers.
Quick FAQs
What are the primary revenue streams for asset managers?
Asset managers generate revenue through management fees, performance-based fees, and other ancillary services.
How do asset managers determine the fees they charge?
Fees vary based on factors such as the size of the fund, investment strategy, and performance track record.
What are performance-based fees and how do they impact revenue?
Performance-based fees are contingent upon the manager’s ability to generate returns above a benchmark. These fees incentivize managers to align their interests with investors.
Asset managers generate revenue through fees charged to clients for managing their investments. These fees can vary based on the type of asset being managed and the level of service provided. In the realm of hospitality, assistant managers in restaurants perform a myriad of duties, including supervising staff , ensuring smooth operations, and maintaining high standards of customer service.
Similarly, asset managers are responsible for safeguarding and growing their clients’ wealth, making informed investment decisions, and providing ongoing portfolio management.
An asset manager typically earns fees based on the value of the assets they manage. Fees can be charged as a percentage of assets under management, a fixed fee, or a combination of both. These fees cover the costs of managing the assets, including research, trading, and administration.
For example, embedded computers are used in ATMs to manage financial transactions. These computers are responsible for verifying the user’s identity, processing the transaction, and dispensing cash. The fees charged by asset managers help to cover the costs of these services, as well as the costs of managing the underlying investments.
Asset managers generate revenue through fees charged to clients for managing their investments. These fees can vary depending on the type of asset being managed and the services provided. The duties of a project manager in an NGO, such as planning, budgeting, and coordinating resources , can provide valuable insights into how asset managers effectively manage their clients’ investments.
An asset manager’s primary revenue stream is derived from fees charged to clients for managing their investments. These fees can vary based on the type of asset and the level of service provided. Additionally, asset managers may also generate income from performance-based incentives if they exceed certain investment targets.
In the context of case management from an empowerment perspective, asset managers can leverage their expertise to empower clients to make informed decisions about their financial futures. By providing personalized guidance and support, asset managers can help clients develop a sense of agency and ownership over their financial well-being, ultimately enhancing their ability to achieve their long-term financial goals.