As an example of an asset management efficiency ratio is the takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with american pop culture language into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
An example of an asset management efficiency ratio is the expense ratio, which measures the percentage of assets under management that are used to cover operating expenses. To effectively manage these expenses, organizations often implement a hierarchical structure with three levels of managers: first-line managers, middle managers, and top managers.
3 levels of managers in an organization have distinct roles and responsibilities, working together to optimize asset management efficiency and drive organizational success. Thus, the expense ratio serves as a key indicator of asset management efficiency, reflecting the organization’s ability to balance operational costs with investment returns.
An asset management efficiency ratio is a valuable tool for evaluating the performance of asset management strategies. It measures the relationship between the return on assets and the cost of managing those assets. By understanding how to calculate and interpret this ratio, investors can make informed decisions about their asset allocation and management strategies.
For example, an asset management efficiency ratio is the ratio of administrative expenses to assets under management. Among the various administrative functions of an office manager , streamlining operations can reduce administrative expenses and improve the efficiency ratio. This can lead to higher returns for investors and a more efficient use of company resources.
Asset Management Efficiency Ratio
In the realm of asset management, where the efficient allocation and utilization of resources reign supreme, the asset management efficiency ratio emerges as a pivotal metric. It serves as a beacon, guiding asset managers towards optimizing their portfolios and maximizing returns while minimizing risks.
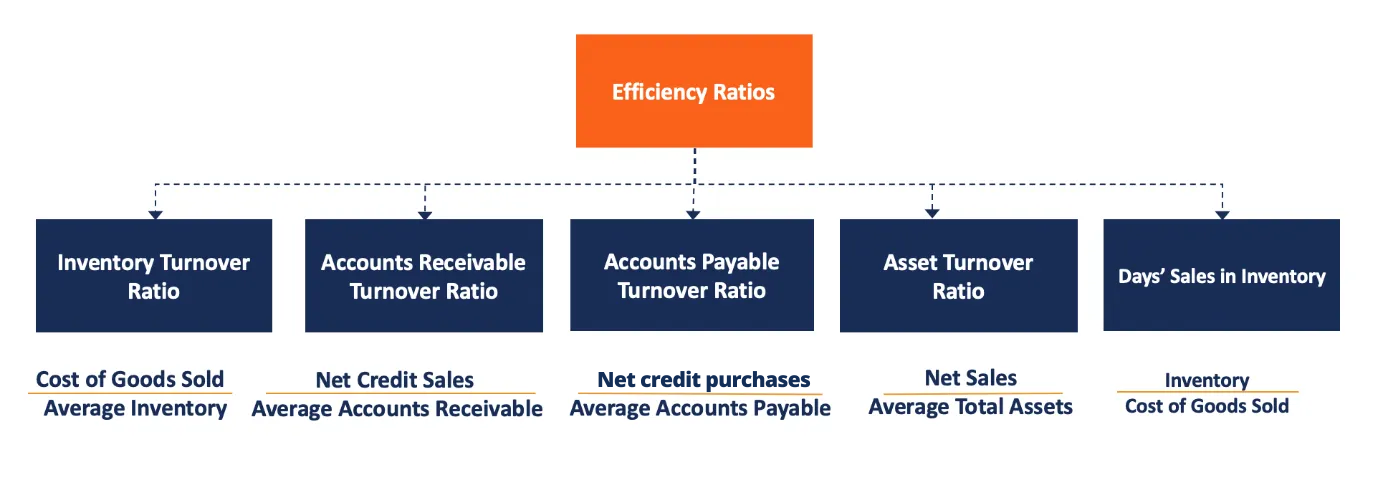
An example of an asset management efficiency ratio is the fixed asset turnover ratio, which measures how efficiently a company uses its fixed assets. An advantage of database management approach is that it can help companies track their assets more effectively and efficiently, which can lead to improved asset management efficiency ratios.
Calculation and Interpretation
The asset management efficiency ratio is a mathematical formula that assesses the relationship between the value of assets managed and the expenses incurred in managing those assets. The formula is expressed as follows:
Asset Management Efficiency Ratio = (Value of Assets Managed) / (Management Expenses)
A higher ratio indicates that the asset manager is effectively utilizing its resources and generating more value relative to the costs incurred. Conversely, a lower ratio suggests that the manager may be incurring excessive expenses or underperforming in terms of asset appreciation.
An example of an asset management efficiency ratio is the turnover ratio, which measures how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate revenue. This ratio is calculated by dividing a company’s net sales by its average total assets. A high turnover ratio indicates that a company is using its assets efficiently, while a low turnover ratio indicates that the company is not using its assets efficiently.
An effective performance management system should be able to track and measure the turnover ratio and other key performance indicators to help companies improve their asset management efficiency.
Factors Affecting the Ratio, An example of an asset management efficiency ratio is the
The asset management efficiency ratio can be influenced by various factors, including:
- Size of the asset portfolio
- Complexity of the assets
- Investment strategy
- Market conditions
- Manager’s skill and experience
Examples and Case Studies
The asset management efficiency ratio is widely used by asset managers, investors, and analysts to evaluate the performance of asset management firms. Here are some examples:
- A mutual fund with a high asset management efficiency ratio may indicate that the fund manager is effectively managing costs and generating strong returns for investors.
- A hedge fund with a low asset management efficiency ratio may suggest that the fund is incurring excessive expenses or underperforming relative to its peers.
Best Practices and Benchmarks
To optimize the asset management efficiency ratio, asset managers should consider the following best practices:
- Negotiating lower fees with custodians and other service providers
- Utilizing technology to automate processes and reduce expenses
- Investing in professional development to enhance investment skills
Industry benchmarks or standards can provide a reference point for asset managers to assess their performance. These benchmarks are typically based on the average efficiency ratios of similar asset managers.
Limitations and Considerations
While the asset management efficiency ratio is a valuable metric, it has certain limitations:
- It does not consider the quality or risk profile of the assets managed.
- It may not accurately reflect the manager’s skill or ability to generate returns.
- It can be distorted by short-term market fluctuations.
To gain a more comprehensive view of an asset manager’s performance, it is important to consider other metrics and qualitative factors in conjunction with the asset management efficiency ratio.
An example of an asset management efficiency ratio is the ability to track inventory levels and usage patterns. This information can then be used to optimize inventory levels and reduce waste. A vendor managed inventory system refers to an arrangement where the supplier manages the inventory levels of the buyer.
This can help to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Summary: An Example Of An Asset Management Efficiency Ratio Is The
In conclusion, an example of an asset management efficiency ratio is the is a powerful tool that can help investors make informed decisions about their asset allocation and management strategies. By understanding how to calculate and interpret this ratio, investors can identify areas for improvement and optimize their portfolio performance.
An example of an asset management efficiency ratio is the ratio of assets under management to the number of employees. This ratio measures how efficiently a company is managing its assets. An Elegant Affair Event Management is a company that specializes in managing events.
They have a team of experienced professionals who can help you plan and execute your event flawlessly. An example of an asset management efficiency ratio is the ratio of assets under management to the number of employees.
FAQ Compilation
What is an asset management efficiency ratio?
An asset management efficiency ratio is a measure of the relationship between the return on assets and the cost of managing those assets.
How is an asset management efficiency ratio calculated?
An asset management efficiency ratio is calculated by dividing the return on assets by the cost of managing those assets.
What does an asset management efficiency ratio tell me?
An example of an asset management efficiency ratio is the fixed asset turnover ratio, which measures how efficiently a company uses its fixed assets to generate revenue. To delve deeper into the intricacies of asset management and engineering management, consider exploring the insightful resource: an elegant puzzle systems of engineering management epub . Returning to the topic of asset management efficiency ratios, it’s crucial to note that they can provide valuable insights into a company’s financial performance.
An asset management efficiency ratio can tell you how efficiently your assets are being managed. A higher ratio indicates that your assets are being managed more efficiently.